1 Introduction
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) incorporates human preferences into AI systems to solve objectives that are difficult to specify explicitly. It rose to prominence by making foundation models more helpful, safe, and usable, and now sits at the center of modern post-training—the collection of methods applied after large-scale pretraining to turn raw next-token predictors into capable assistants. Within post-training, instruction/supervised fine-tuning establishes basic instruction following, preference fine-tuning (where RLHF is the dominant approach) aligns models to nuanced human values and style, and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards targets tasks with clear, checkable objectives. This chapter motivates why RLHF became essential and frames it as the technique that catalyzed today’s broader post-training toolbox.
Operationally, RLHF follows a three-step pipeline: train an instruction-following base model, collect human preference data to learn a reward model, and optimize the policy against that reward using an RL optimizer. Behaviorally, RLHF shifts models from raw continuations to concise, cooperative answers, shaping tone, empathy, and format in ways that improve reliability and user experience. Unlike instruction tuning’s per-token objective, RLHF learns at the response level with contrastive signals about better versus worse outputs, which tends to generalize more robustly across domains. These advantages come with challenges: reward models are proxies that can induce over-optimization and length bias, the process is costlier in data and compute, and strong results require a good starting model plus careful regularization. RLHF is thus most effective as one stage in a multi-stage post-training recipe.
RLHF has powered progress across control tasks, summarization, instruction following, web question answering, and safety, and its practice has evolved alongside open and closed efforts—from early instruction-tuned imitators, through skepticism about the need for RLHF, to the rise of direct alignment methods that simplify preference optimization. The chapter advances an elicitation view of post-training: much of a model’s latent capability exists after pretraining, and well-designed post-training extracts and amplifies it, often yielding large gains without changing the base model itself—while still depending on data scale and thoughtful design choices. Looking forward, preference fine-tuning remains foundational even as newer RL approaches for verifiable rewards and reasoning accelerate. The book aims to clarify trade-offs, offer practical implementation guidance, and build the intuition needed to reproduce, extend, and responsibly apply RLHF in real systems.
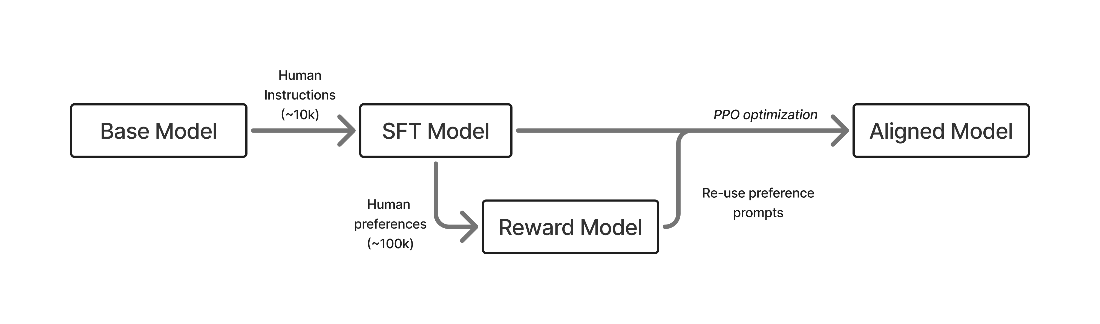
A rendition of the early, three stage RLHF process: first training via supervised fine-tuning (SFT, chapter 4), building a reward model (RM, chapter 5), and then optimizing with reinforcement learning (RL, chapter 6).
Summary
- RLHF incorporates human preferences into AI systems to solve problems that are hard-to-specify programmatically, and became widely known through ChatGPT’s breakout, which made the capabilities of language models more approachable.
- The basic RLHF pipeline has three steps: instruction fine-tuning to teach the model to follow the question-answering format, training a reward model on human preferences, and optimizing the model with RL against that reward.
- RLHF is known to primarily change the style, tone, and format of model responses – making them more helpful, warm, and engaging. But it’s not “just style transfer”: RLHF also improves benchmark performance, though over-optimization (e.g., excessive length or chattiness) can harm capabilities in other domains.
- The elicitation theory of post-training suggests that base models contain latent potential, and post-training’s job is to extract and cultivate that intelligence into useful behaviors.
- RLHF is one component of modern post-training, alongside instruction fine-tuning (IFT/SFT) and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR), used together in an intertwined manner to craft particular training recipes.
FAQ
What is RLHF and why is it important?
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) incorporates human preferences into AI training to handle objectives that are hard to specify directly. It became essential as AI systems moved from research benchmarks to user-facing tools, where nuanced, often inexpressible human preferences matter.How does the classic RLHF pipeline work?
- Train a base instruction-following model via Instruction/Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT/IFT).- Collect human preference data and train a reward model that scores outputs by preference.
- Optimize the model with reinforcement learning, sampling responses and improving them using the reward model’s scores.
Where does RLHF fit within modern post-training?
Post-training is the many-stage process after large-scale pretraining. It commonly includes: (1) SFT/IFT to teach format and instruction-following, (2) Preference Fine-tuning (PreFT), where RLHF dominates and aligns models to human preferences and style, and (3) RL with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to boost performance on tasks with clear, checkable rewards.How does RLHF change a model’s behavior compared to a base model?
Base models tend to continue text as found on the internet. RLHF shifts outputs toward concise, directly helpful, user-oriented answers with clearer tone, formatting, and conversational responsiveness—improving reliability, warmth, and engagement.How is RLHF different from instruction fine-tuning?
Instruction fine-tuning uses per-token supervision to imitate reference text and teach features/format. RLHF makes response-level updates using preference signals (often contrastive), teaching the model what is better or worse rather than exactly what to copy, and generally transfers better across domains.What are the main challenges and costs of RLHF?
- Training robust reward models lacks universal best practices and depends on the domain.- Risk of over-optimization (Goodharting) against proxy rewards, requiring strong regularization.
- Biases such as length bias can emerge.
- It is more expensive in data, compute, and time, and works best starting from a strong instruction-tuned base.
 The RLHF Book ebook for free
The RLHF Book ebook for free