1 Making Sense of Application Security
Security has become a universal concern as breaches and vulnerabilities regularly impact users and organizations worldwide. This chapter explains that weaknesses can exist at every layer of the computing stack—from hardware to browser code—making protection a shared responsibility across roles. It sets a practical tone for developers: understand real-world stakes, navigate tradeoffs among speed, cost, and safety, and gain working competence with cryptography, authentication, and secure communication to prevent tomorrow’s headlines.
Using a simple SQL injection example, the chapter demonstrates how mishandling untrusted input turns into exploitable behavior, and how defenses like parameterized queries reflect a security-first mindset. It then maps where security lives in a developer’s workflow—design, implementation, dependency management, configuration, deployment, and maintenance—while showing how corporate expectations and audits shape day-to-day engineering choices. A key message is that libraries and tools are necessary but not sufficient: understanding the underlying standards, protocols, and patterns they implement enables correct configuration, faster debugging, effective DevSecOps practices, and safer defaults.
Because modern software depends on complex supply chains, the chapter underscores risks from vulnerable or compromised dependencies and promotes continuous scanning, rapid patching, and disciplined reliance on stable public APIs to keep upgrades practical. It situates developers within a broader security ecosystem—spanning mathematicians, cryptographers, standards authors, library and framework engineers, InfoSec teams, auditors, and hackers—clarifying what developers must know to collaborate and ship securely without specializing in every field. It concludes with a learning path that builds from fundamentals to applied standards so you can design with identity in mind, protect data in transit and at rest, detect and fix common flaws, pass audits confidently, and deliver software users can trust.
Headlines showcasing major recent data breaches and security vulnerabilities, emphasizing the widespread impact on millions of users and the persistent threat to digital security.
Layers at the top depend on the layers below them. All the layers are required to produce secure application. The standards, protocols, and patterns used to secure applications are the primary focus of this book, they are the foundation that you need to use security libraries in your application effectively.
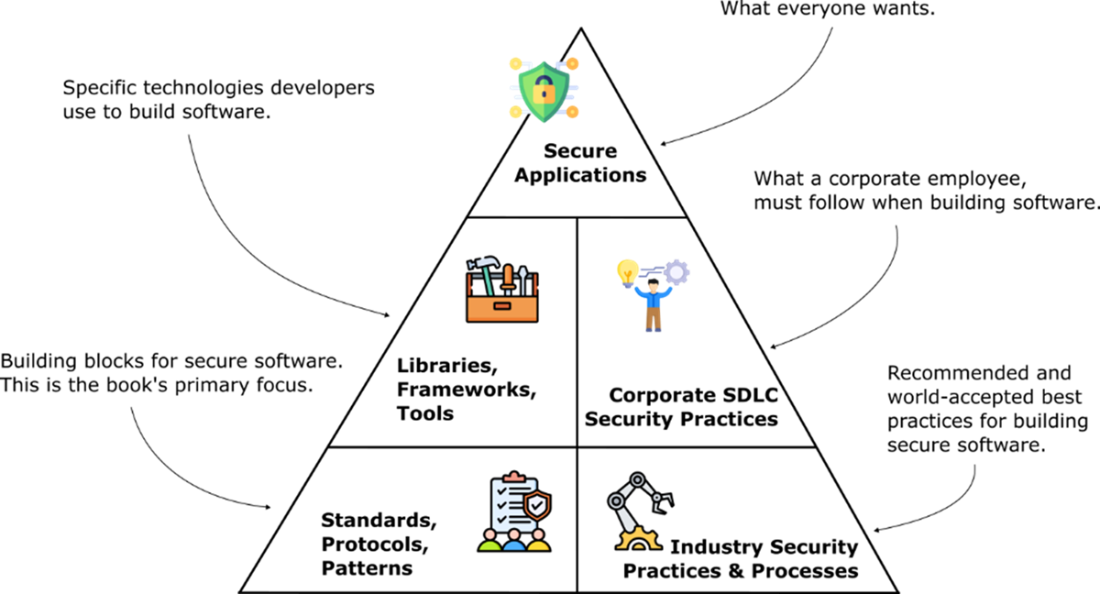
While developers often focus on libraries, frameworks, and tools at the mid-level, true security stems from foundational knowledge of standards, protocols, and patterns, as well as adherence to corporate and industry security practices. Bridging the gap between these layers leads to more effective and secure development.
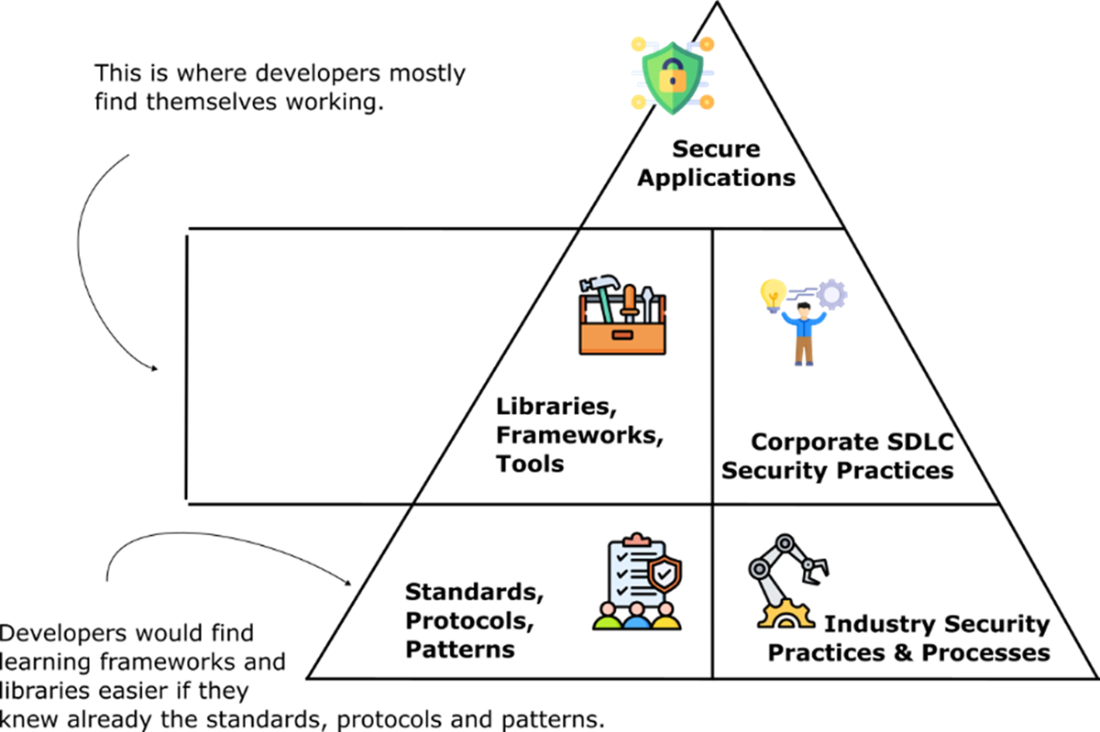
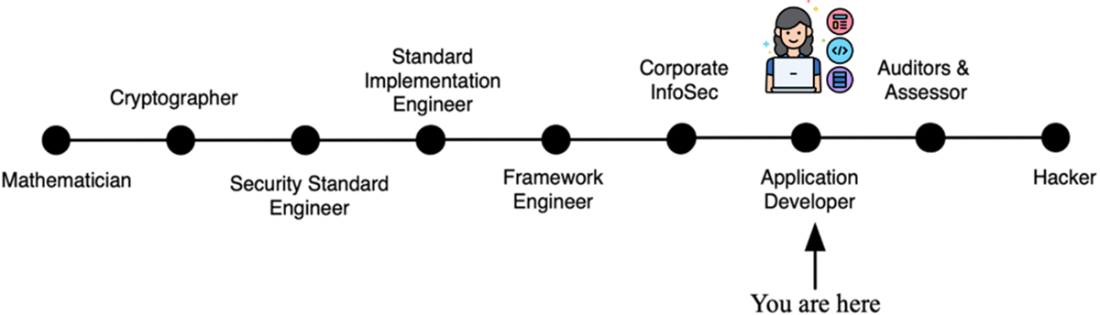
The spectrum of technical roles involved in computer security roles and responsibilities
Summary
- Security vulnerabilities can exist at every layer of the stack, from hardware (e.g., Meltdown, Specter) to application code.
- Security is everyone’s responsibility, not just InfoSec teams - developers play a central role.
- The business impact of breaches is massive (e.g., Marriott, Equifax), often costing millions or even billions.
- Security libraries (like Spring Security) are essential but hard to use unless you understand the underlying standards and protocols.
- Supply chain attacks (e.g., Equifax Apache Struts, Event-Stream Bitcoin theft) highlight the need for vigilance in managing dependencies.
- Automated vulnerability scanning in CI/CD pipelines is a best practice to detect and fix issues quickly.
- Stick to published APIs in libraries to ensure maintainability and security over time.
- Different roles contribute to security: mathematicians, cryptographers, standards engineers, framework engineers, InfoSec teams, auditors, and developers.
- Developers don’t need deep expertise in all these roles, but they must understand enough to apply standards and use libraries correctly.
- This book teaches developers the foundations (cryptography, protocols, standards) so they can confidently build secure, reliable applications.
 Software Security for Developers ebook for free
Software Security for Developers ebook for free