1 Introduction
Welcome to a pragmatic take on learning PostgreSQL through the lens of real-world missteps. The chapter sets the stage by explaining why PostgreSQL matters now: it is a robust, extensible, and increasingly enterprise-ready database backed by a strong, open, and community-driven governance model that avoids vendor lock-in. Its permissive licensing, thriving ecosystem, and broad adoption across industries—from OLTP to analytics—make it a compelling platform, further amplified by extensions that address specialized needs. This context underscores the book’s central premise: mistakes are valuable learning opportunities.
The chapter then explains why talking about mistakes is essential. As PostgreSQL’s popularity grows, users often import habits from other databases, misread or lack context from documentation, pick the wrong tool or data type, or make choices that don’t scale. Common pitfalls include expecting production-ready defaults, relying on implicit type coercions, assuming behaviors from other systems, leaning on outdated standard features, or neglecting best practices around schema design, concurrency, high availability, disaster recovery, and security. Raising awareness helps prevent costly incidents, saves time, protects data, fights anti-patterns, promotes proven solutions, and ultimately helps teams get the most out of PostgreSQL while preserving its reputation.
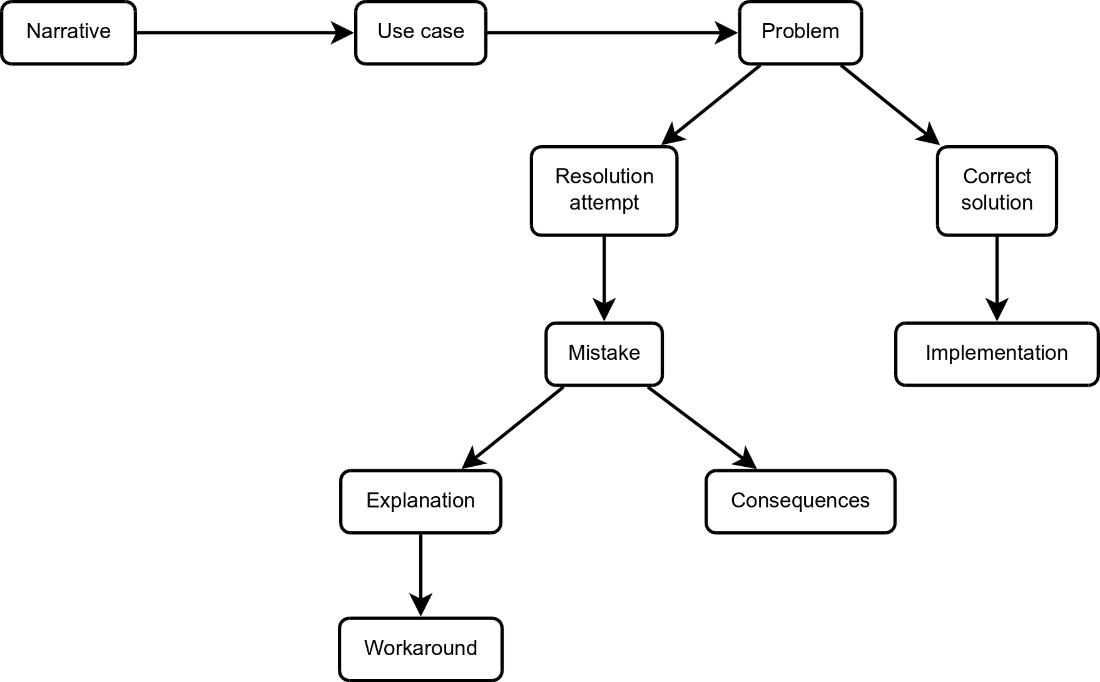
Finally, the chapter outlines how the book works. Each topic starts with a narrative that frames the use case, shows a flawed attempt, analyzes why it’s wrong and its consequences, and then presents a correct solution with practical steps and code. It promotes a clear mental model of PostgreSQL as a client-server, multi-process system and uses PostgreSQL 17 for demonstrations. A concise example shows how a partial index can outperform a broad index when only a small subset of rows matters, illustrating the book’s problem-to-solution flow. A retail-themed sample database (Frogge Emporium) underpins the examples, and readers can expect to develop a stronger grasp of core principles, avoid pitfalls, and apply best practices confidently.
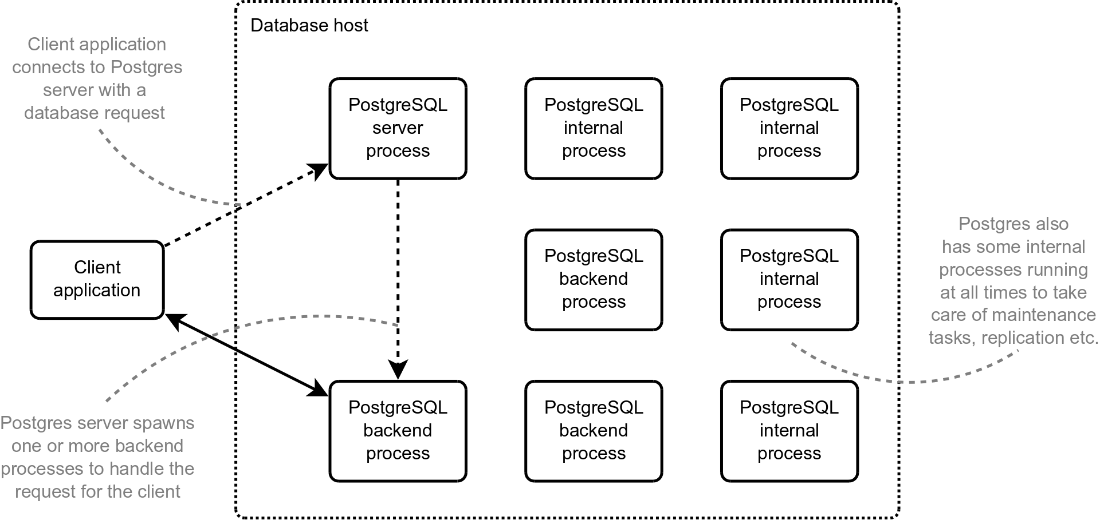
How the PostgreSQL client-server architecture works
How "PostgreSQL Mistakes and How to Avoid Them" works
Summary
- PostgreSQL is a powerful, free and standards-compliant database that is disrupting the industry and gaining in popularity every day.
- It’s important to learn about Postgres mistakes (and from those mistakes) to save time and effort and safeguard your data.
- Raising awareness of potential issues benefits everyone.
- You need to understand how Postgres works and in what ways it is different from other DBMSs in order to avoid making mistakes, especially if you are coming from another system — not all databases are created equal.
- PostgreSQL has a client-server multi-process architecture and this forms important context for the rest of this book.
- Following best practices and examining the documentation carefully will guide you to the correct technical solution for your problem.
- This book uses a use case narrative, accompanied by code, to demonstrate how you can make a mistake and prevent or recover from it.
FAQ
What is this book about, and how is it different from a tutorial or admin guide?
This book focuses on real-world PostgreSQL mistakes, why they happen, their consequences, and how to avoid or correct them. It is not a step-by-step tutorial or an administration manual; instead, it uses practical scenarios to teach better decisions and practices.Why does learning about PostgreSQL matter right now?
PostgreSQL is a robust, extensible, feature-rich database that is steadily displacing proprietary systems. It has strong community and commercial support, frequent new enterprise features, and many hosted/DBaaS options—making it a strategic choice for modern applications.How do PostgreSQL’s community model and license benefit users and businesses?
PostgreSQL is community-led and released under a permissive license that avoids vendor lock-in. You can base products on it (open source or proprietary), and sell support, hosting, or training without restrictive licensing. Project governance prevents single-entity control, maintaining long-term license stability.What kinds of workloads and extensions showcase PostgreSQL’s versatility?
PostgreSQL powers OLTP and OLAP workloads across industries such as finance, retail, logistics, media, government, and space. Popular extensions expand capabilities further: PostGIS (GIS), Citus (columnar/distribution), TimescaleDB (time series), and pgvector (vector search).Why talk about PostgreSQL mistakes, and what’s the benefit of avoiding them?
Common pitfalls stem from importing habits from other DBMSs, misreading docs, choosing the wrong tool, or making choices that don’t scale. Avoiding them helps you:- Save time and effort
- Protect data
- Future-proof designs
- Avoid anti-patterns
- Prefer standard, well-known solutions
- Build teamwide best-practices awareness
- Get the most from PostgreSQL—and protect its reputation
What are the typical kinds of PostgreSQL mistakes people make?
- Bringing assumptions from other DBMSs (e.g., expecting a USER to auto-create a same-named SCHEMA, or silent type coercions like 0/1 into BOOLEAN)
- Misunderstanding PostgreSQL’s fit (using it as embedded, DIY-distributed, log server, bulk video store, in-memory cache, or graph DB without weighing trade-offs)
- Misreading documentation (technical tone, missing context, or using the wrong version’s docs)
- Using SQL Standard relics that aren’t practical or consistent across systems
- Ignoring best practices for schema design, concurrency, HA/DR, and security
 PostgreSQL Mistakes and How to Avoid Them ebook for free
PostgreSQL Mistakes and How to Avoid Them ebook for free