1 Understanding the world of MongoDB
The chapter introduces the shift toward next-generation databases and positions MongoDB as a versatile, scalable document database built for modern application demands. It explains how MongoDB’s flexible document model, powered by BSON and accessed through an intuitive Query API, enables rapid development and efficient data access across diverse workloads. The narrative sets the stage by highlighting core capabilities—secondary indexes, aggregations, geospatial queries, and real-time change streams—while noting Atlas as the managed platform that extends MongoDB with automation, security, and multi-cloud resiliency.
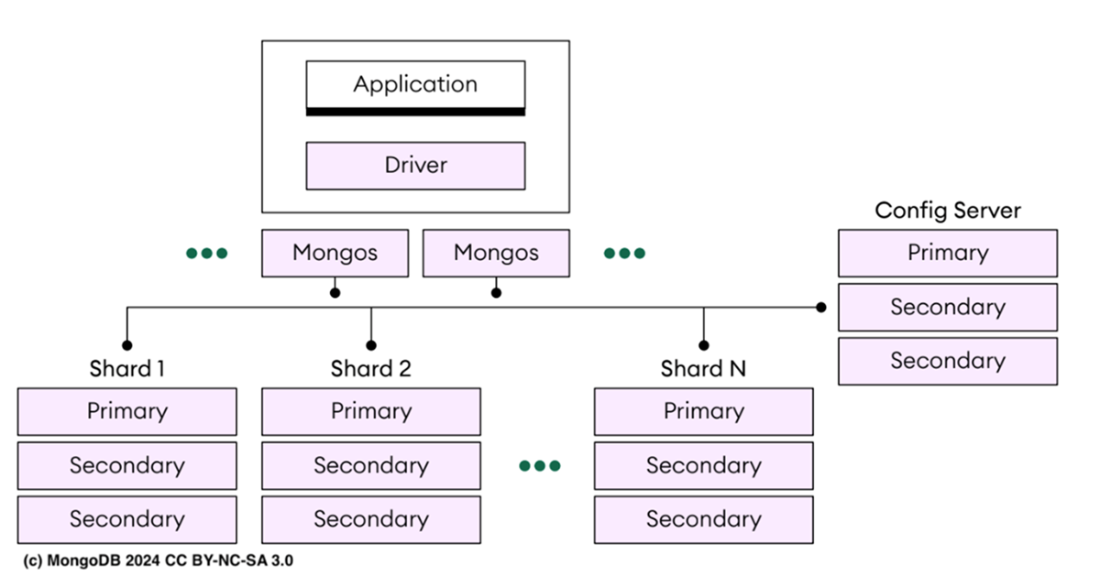
It then examines the document-oriented data model in depth, contrasting flexible schemas with rigid relational designs and showing how embedding and arrays reduce joins and read operations. Readers get a first look at common MongoDB queries and updates, as well as performance-oriented features like indexes, time series collections, TTL indexes, and capped collections. The chapter also outlines horizontal scaling through sharding, describing how self-contained documents map well to distributed systems and summarizing the roles of query routers, config servers, and shard replica sets, including operational simplifications introduced in MongoDB 8.0.
Finally, the chapter surveys the wider MongoDB ecosystem and Atlas platform, emphasizing how Atlas augments the core server with full-text search, vector search for generative AI and RAG, stream processing, data federation, and a SQL interface—all unified under the same Query API. It highlights Atlas automation, backups, and security as foundations for reliable, cloud-native deployments across AWS, Azure, and GCP. The discussion closes with a note on MongoDB 8.0’s enhanced TCMalloc, which uses per-CPU caches to improve performance and resilience under heavy, concurrent workloads.
MongoDB's sharding architecture enables horizontal scaling by distributing data across multiple servers.
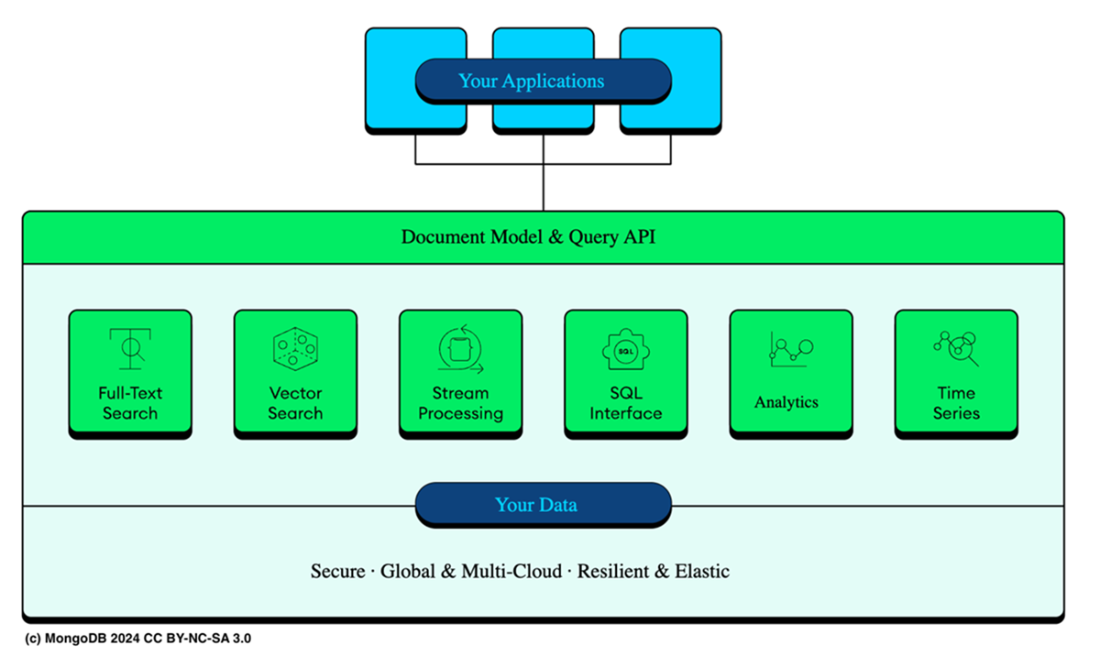
High-level architecture of the MongoDB multi-cloud Atlas data platform, with its key components such as the Document Model, Unified Query API, and foundational features like security, global multi-cloud capabilities, resilience, and elasticity. MongoDB supports diverse functionalities like Full-Text Search, Vector Search, Stream Processing, SQL Interface, Analytics, and Time Series, all of which integrate with your applications and data across various environments.
Summary
- In modern software development, objects representing real-world entities need to be stored permanently for future use, a process called persistence. Document databases like MongoDB simplify this by allowing direct storage of objects without significant data transformation, supporting intuitive querying.
- Unlike traditional relational databases with strict schemas, document databases like MongoDB offers a flexible schema, allowing dynamic structures with varied fields. This flexibility makes them ideal for rapid development and scalable scenarios, such as content management systems and real-time analytics, streamlining data management and reducing retrieval costs.
- MongoDB uses BSON (Binary JSON) to store objects, extending JSON with additional data types like dates and binary data. This allows it to handle complex structures effectively. Most programming languages offer compatible structures like maps or dictionaries, which MongoDB leverages for efficient data manipulation and retrieval.
- To interact with this data, you can use the MongoDB Query API, which is effective and versatile for all database operations. The Query API is designed to be intuitive, making it easy to express both simple and complex queries.
- MongoDB is optimized for scaling out, using its document-oriented model and sharding to distribute data across multiple servers. Sharding automates data balancing and load distribution, simplifying scalability management. This allows MongoDB to handle large datasets and high throughput. Adding new machines is seamless, as MongoDB intelligently redistributes data across the cluster.
- MongoDB is a general-purpose database available as a free Community Edition and the advanced MongoDB Enterprise, which offers enhanced security, operational tools, and management capabilities. Enterprise features include encrypted storage, Kerberos and LDAP authentication, auditing, Ops Manager, BI Connector, and Enterprise Operator for Kubernetes.
- MongoDB Atlas, a fully managed cloud service, simplifies MongoDB setup, scaling, and management while adding exclusive cloud features. Over the past few years, Atlas has evolved from a database-as-a-service to a full platform, significantly expanding the core MongoDB server's capabilities with a comprehensive suite of features and services for the entire application development lifecycle.
- MongoDB 8.0 introduces a new version of TCMalloc, which uses per-CPU caches instead of per-thread caches. This change helps to reduce memory fragmentation and enhances the database's ability to handle heavy workloads more effectively.
- The MongoDB Query API is the primary method for interacting with MongoDB data. It allows for flexible and efficient querying of documents through filters, projections, and sorting to etrieve the specific data you need. You can use the Query API to perform queries in MongoDB in two main ways: CRUD operations and Aggregation Pipelines.
 MongoDB 8.0 in Action, Third Edition ebook for free
MongoDB 8.0 in Action, Third Edition ebook for free