1 Introduction to AI in Finance
Artificial intelligence has moved from the margins to the center of modern finance, shifting the industry’s talent needs, operating models, and competitive dynamics. From global banks to fintech startups, institutions now treat AI as a strategic imperative for allocating capital, managing risk, and scaling personalized services in a data-rich, highly regulated environment. The chapter frames AI in finance as adaptive, data-driven intelligence—spanning machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing—that detects patterns beyond static rules, while acknowledging finance’s unique constraints around compliance, explainability, precision, and continuous market change.
The chapter organizes AI’s impact into four practical pillars: managing risk and ensuring compliance, extracting market intelligence, enhancing customer experiences, and improving operational efficiency. Concrete examples illustrate the shift: AI-driven underwriting that taps real-time signals, AML systems that cut false positives, generative AI that synthesizes research for wealth managers, embedded finance that enables instant, risk-aware transactions, and automation that reconfigures back-office workflows. Together, these uses show AI delivering sharper risk views, faster insights, tailored interactions, and leaner operations—reshaping both customer outcomes and cost structures.
To build such systems, the chapter introduces a four-layer framework: the Data Asset layer (secure, compliant, high-quality data and domain features), the Modeling layer (fit-for-purpose models with retraining and explainability), the Strategy & Monitoring layer (policies, thresholds, fairness checks, and drift detection aligned to business goals), and the Application layer (user-facing decisions, workflows, and feedback loops). A credit scoring workflow threads these layers end-to-end, showing how raw data becomes real-time lending actions and ongoing portfolio management. The chapter closes with a pragmatic toolset—Python, scikit-learn, Keras/TensorFlow, optional LLM integrations, Airflow for orchestration, and Evidently for monitoring—and a hands-on learning path that emphasizes repeatable principles over one-off demos, preparing readers to ship robust, compliant financial AI solutions.
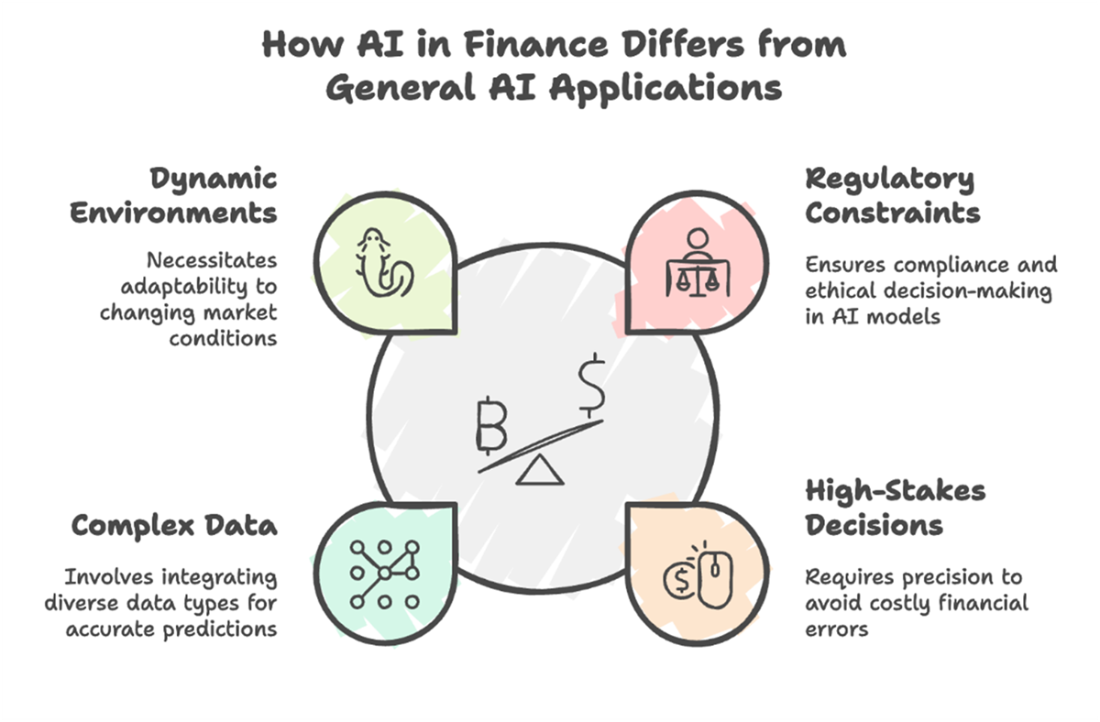
How AI in finance differs from general AI applications. Unlike many industries, finance requires continuous adaptation to changing markets, strict regulatory compliance ensuring fairness and explainability, uncompromising precision to handle high-stakes decisions, and the integration of diverse, complex data. These conditions shape every aspect of building and deploying effective AI-driven financial solutions.
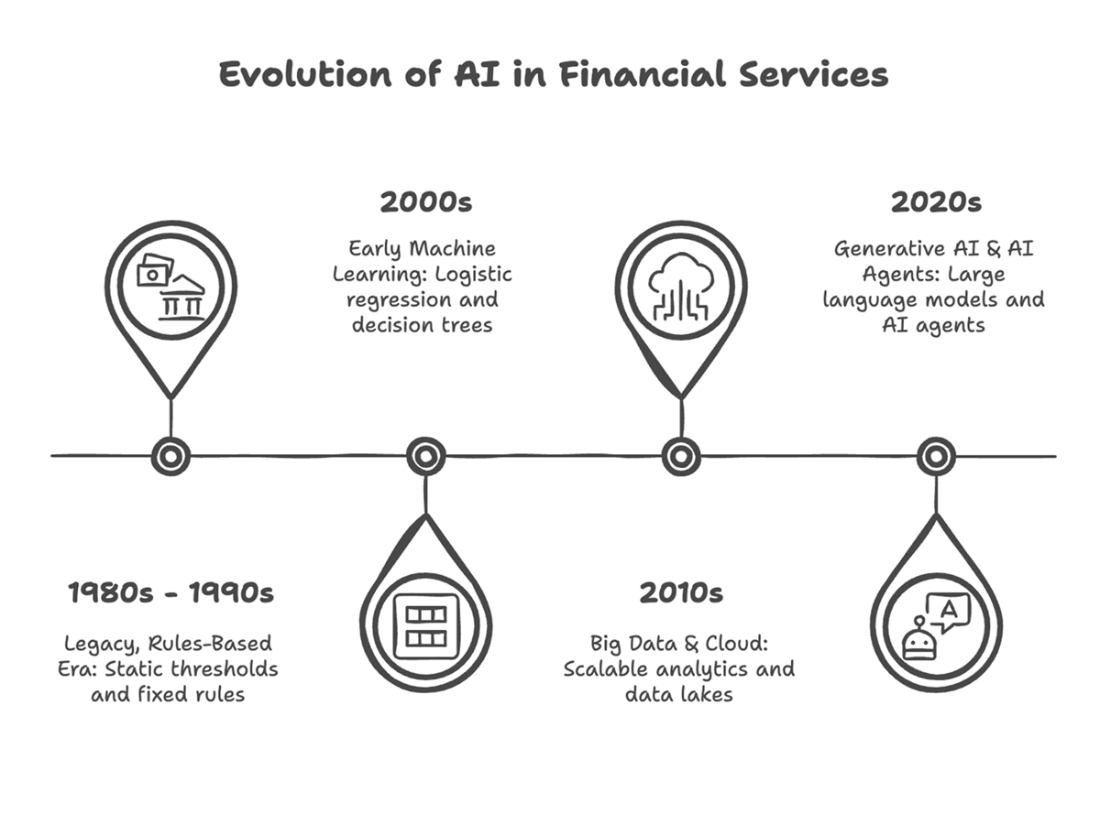
Evolution of AI in Financial Services. This timeline illustrates four major milestones in the industry's journey, from the static, rules-based systems of the 1980s and 1990s to today's generative AI and autonomous agents. Each phase—early machine learning, the rise of big data and the cloud, and the current wave of large language models—expanded AI's capabilities and its impact on the competitive landscape.
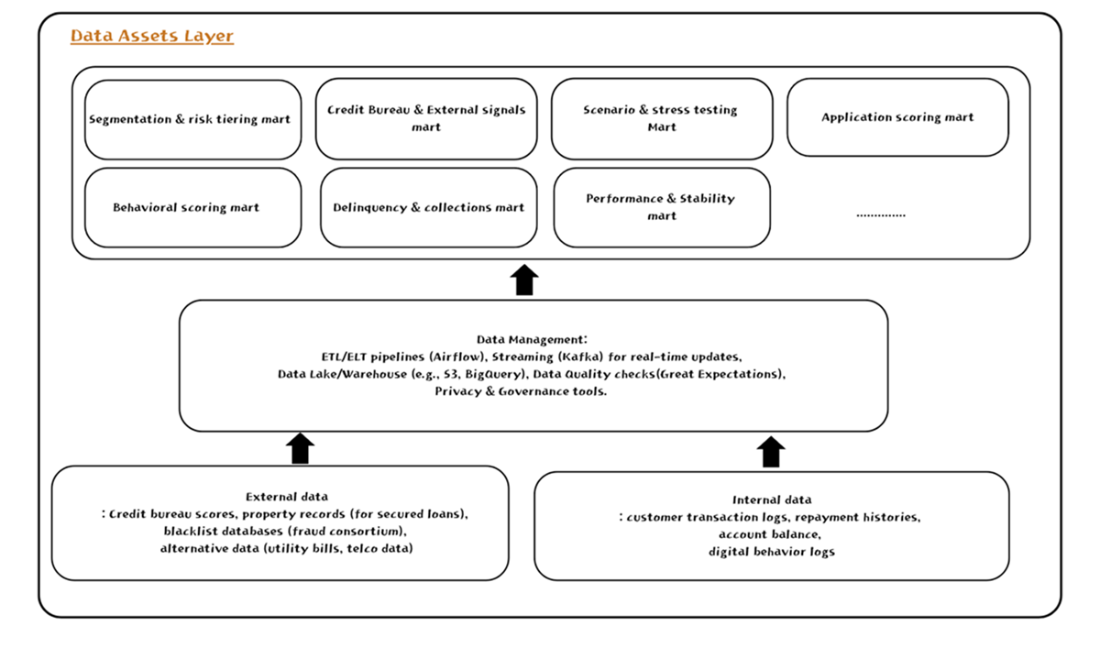
The Data Asset Layer. This figure illustrates how raw data—repayment histories, credit bureau snapshots, and alternative signals—flows into specialized data marts. Ensuring data lineage, access control, and regulatory compliance are critical steps before modeling. By creating consistent, domain-focused features, the Data Asset Layer provides a solid foundation for accurate credit decisions.
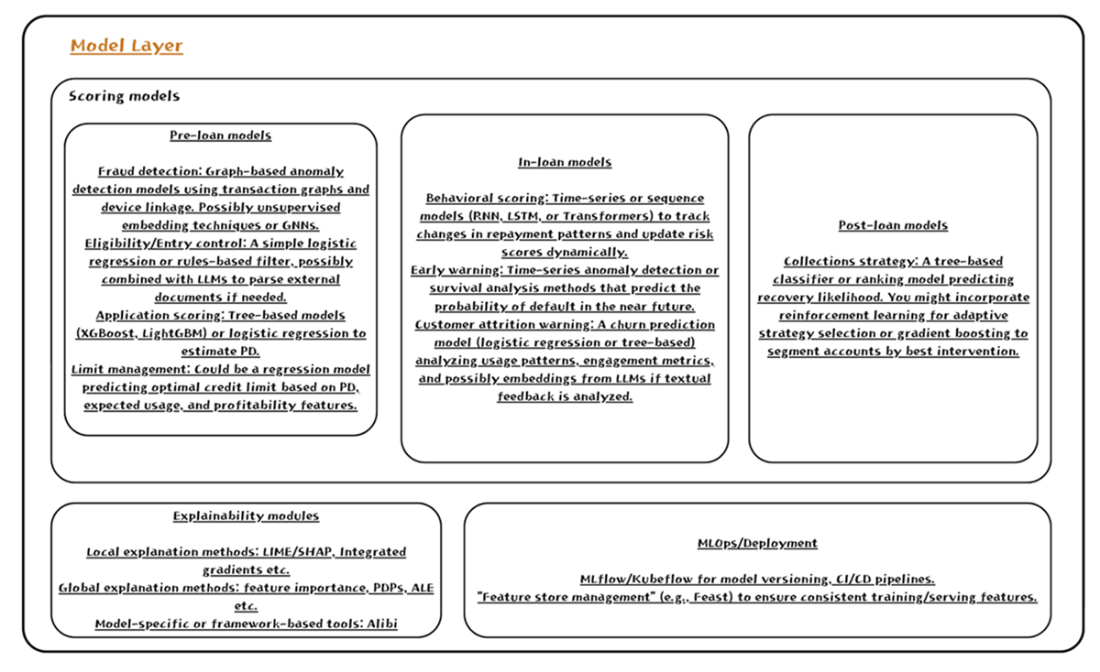
The Modeling Layer. Here, AI models turn curated features into default probabilities, fraud signals, or risk segments. Explainability tools (e.g., LIME or SHAP) offer transparency into each factor’s influence on the final score. Ongoing MLOps practices—such as scheduled retraining or hyperparameter optimization—help keep models current in shifting economic climates.
The Strategy & Monitoring Layer. Domain metrics, rate caps, and threshold policies shape how raw scores become lending actions. Ongoing monitoring detects data or concept drift, ensuring the model’s real-world performance remains stable. A/B testing and other experimentation approaches allow teams to refine credit strategies without risking large-scale exposure.

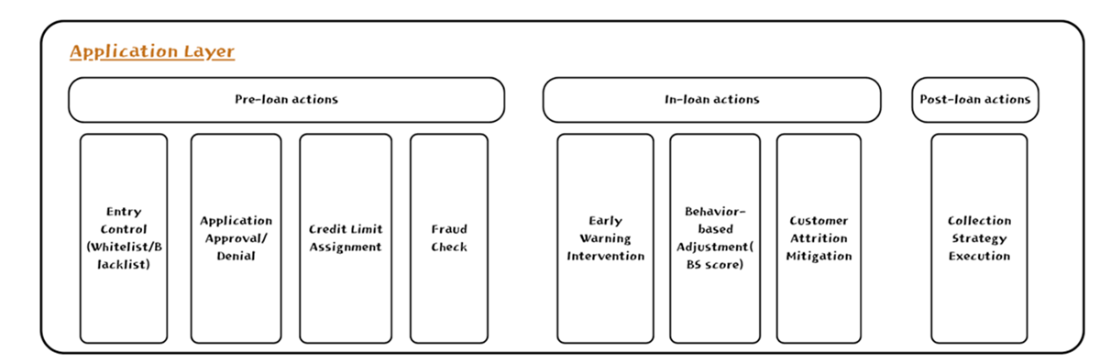
The Application Layer. Loan officers, collection agents, and end customers interact with AI-driven outcomes via dashboards or real-time notifications. By bridging front-end systems (like customer portals) and back-end rule engines, actions like approvals, limit changes, or fraud checks happen seamlessly. Because it’s closely tied to monitoring feedback loops, the Application Layer can adapt quickly to new data or policy shifts.
Summary
- AI in finance integrates data-driven modeling techniques into traditional workflows, enabling improved risk assessment, enhanced customer experiences, advanced trading strategies, and more streamlined operations.
- Understanding core building blocks—Data Asset, Modeling, Strategy & Monitoring, and Application Layers—helps break down complex AI systems into manageable parts.
- A concrete example in credit scoring shows how these layers interact: raw data transforms into predictive insights, which then guide policies and final lending decisions.
- Tools and technologies like Python, ML/DL frameworks, and optional orchestration and monitoring tools provide a flexible, accessible stack for building and maintaining financial AI solutions.
- This book teaches AI in finance through hands-on projects, real-world datasets, domain-specific metrics, and evolving model lifecycles—equipping you to adapt these methods beyond the examples given.
- By the end of Chapter 1, you know what to expect: practical guidance, multiple scenarios, ongoing refinement, and a focus on integrating AI into real financial operations for lasting, scalable impact.
FAQ
What does “AI in finance” mean, and why does it matter?
AI in finance uses machine learning, deep learning, NLP, anomaly detection, and related methods to analyze rich, diverse data and make adaptive decisions. It moves the industry from fixed rules to data-driven intelligence, improving credit decisions, fraud detection, investment insights, and customer experiences in a high-stakes, regulated setting.Why is adopting AI now a competitive imperative for financial institutions?
Decades of progress—from rules-based systems to big data, cloud, and now generative AI and autonomous agents—have lowered barriers and raised competitive pressure. Embedded finance and AI agents are enabling new business models, prompting firms to automate operations and upskill workforces or risk falling behind.How do AI applications in finance differ from general AI apps?
Finance demands continuous adaptation to volatile markets, strict regulatory compliance with fairness and explainability, uncompromising precision for high-stakes decisions, and integration of complex, heterogeneous data (structured, unstructured, streaming, cross-border). These constraints shape design, deployment, and governance.What are the four main pillars of AI use cases in finance?
- Risk & Compliance: Dynamic credit risk, AML/fraud detection (e.g., Toast underwriting; Danske Bank AML false-positive reduction).
- Investment & Market Intelligence: Synthesizing alt data and research (e.g., Morgan Stanley’s generative AI assistant).
- Customer Experience: Personalization and embedded finance (e.g., Uber instant payouts with real-time risk checks).
- Operational Efficiency: Automating document processing and workflows (e.g., workforce impacts like at BPER Bank).
What is the four-layer approach to building financial AI systems?
- Data Asset Layer: Curate secure, compliant, high-quality domain data and features.
- Modeling Layer: Train/evaluate models to produce predictions and signals.
- Strategy & Monitoring Layer: Convert signals into policies; monitor drift, risk, and fairness.
- Application Layer: Deliver decisions to users and operations; close the feedback loop.
How does the credit scoring workflow illustrate these layers end-to-end?
- Data: Aggregate internal and external sources into a credit data mart with lineage, privacy, and quality controls.
- Modeling: Use methods like logistic regression or XGBoost; evaluate with K-S and AUC; apply explainability tools.
- Strategy & Monitoring: Set thresholds, run A/B tests, watch drift, and check fair lending impacts.
- Application: Make instant approvals, request docs, adjust limits, and feed outcomes back for continuous improvement.
Which data sources and features are most important in financial AI?
Core sources include transaction logs, market tick data, customer profiles/credit histories, regulatory filings, and alternative signals (sentiment, macro, weather, satellite). Effective feature engineering—e.g., volatility for investments, velocity features for fraud, seasonality in spending—paired with compliance (GDPR, CCAR), lineage, and access control is critical.Which models, metrics, and explainability methods are commonly used?
- Models: Logistic regression, gradient-boosted trees, time-series, graph methods, deep learning, and LLMs for unstructured text.
- Metrics: K-S (credit), AUC, precision/recall (fraud), Sharpe (portfolios).
- Explainability: SHAP, LIME to interpret factor contributions.
- MLOps: Scheduled retraining, hyperparameter tuning, and drift detection to keep models current.
What tools, data, and infrastructure do I need to follow along?
- Stack: Python, scikit-learn, Keras/TensorFlow; optional OpenAI API for LLMs.
- Data/Compute: Public datasets (e.g., Kaggle); a standard laptop; optional cloud.
- Ops (optional): Apache Airflow for orchestration; Evidently AI for monitoring and drift.
- Dev: Any IDE (VS Code, PyCharm, Jupyter) and a public GitHub repo with code.
 Financial AI in Practice ebook for free
Financial AI in Practice ebook for free