1 What makes conversational AI work?
This chapter sets the stage for building conversational AI that users actually want to use. It defines conversational AI and the main solution types—question answering, process-oriented workflows, and routing—and explains why so many assistants fail: they misread intent, impose unnecessary complexity, or trigger immediate opt-outs. The chapter introduces a simple, universal flow for successful systems: understand what the user wants, gather only the information needed, and deliver the result quickly and ethically. It emphasizes user-centered design, the interplay between intent models, dialogue, and APIs, and the importance of designing for the channel and context to reduce friction and personalize help.
The chapter then introduces generative AI as a complementary tool to classic techniques. Large language models can bolster intent understanding, simplify and improve copy, power retrieval-augmented answers, and accelerate builder workflows such as data augmentation and dialogue drafting. Because LLMs can be biased or hallucinate, the chapter stresses practical guardrails: choosing appropriate models and training data, adding contextual prompts, pre- and post-filtering for unsafe content, and keeping humans in the loop when risk is high. It also highlights the need to experiment with models and parameters for each task, optimizing for both performance and safety.
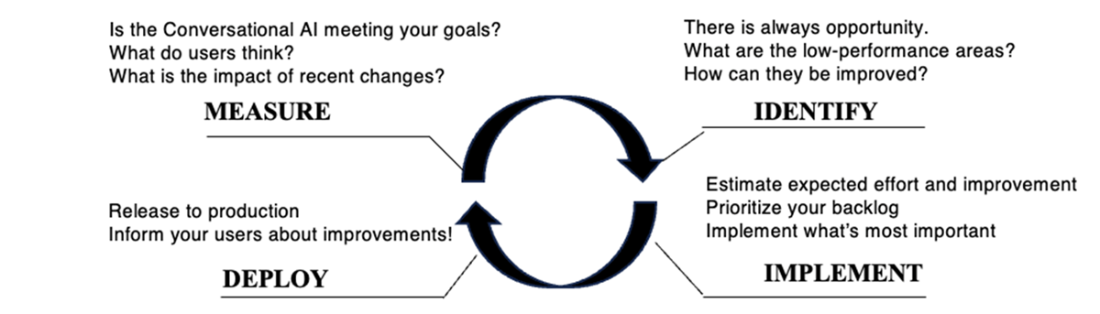
Finally, the chapter advocates a disciplined, continuous improvement cycle: measure, identify a problem tied to business outcomes, implement targeted fixes, deploy, and repeat. Small, incremental changes are preferred over large, risky overhauls because they deliver value sooner, are easier to diagnose, and create more learning opportunities. Success depends on improving the full chain—engagement, understanding, and fulfillment—and communicating progress in business terms. Teams should tie technical work to metrics like containment, average handle time, time to resolution, and customer satisfaction, ensuring stakeholders see clear, compounding value from ongoing enhancements.
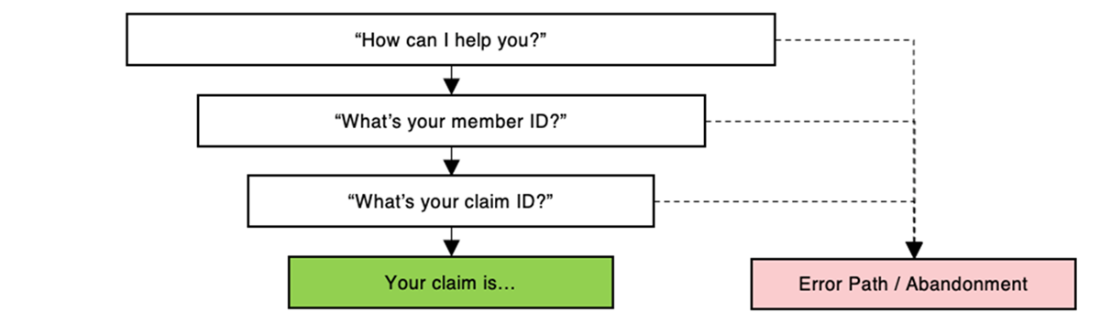
A painful chat experience with a process-oriented bot that puts cognitive burden on the user. The AI has not provided any value in three conversational turns.

A delightful experience that uses context and reasonable assumptions to complete the user's goal quickly. The context could be loaded from a log-in process (chat) or from caller phone number (voice).

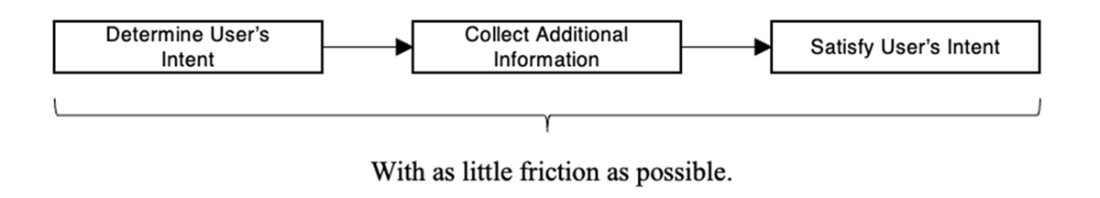
Flow diagram for conversational AI. In many use cases “additional information” includes user profile data.
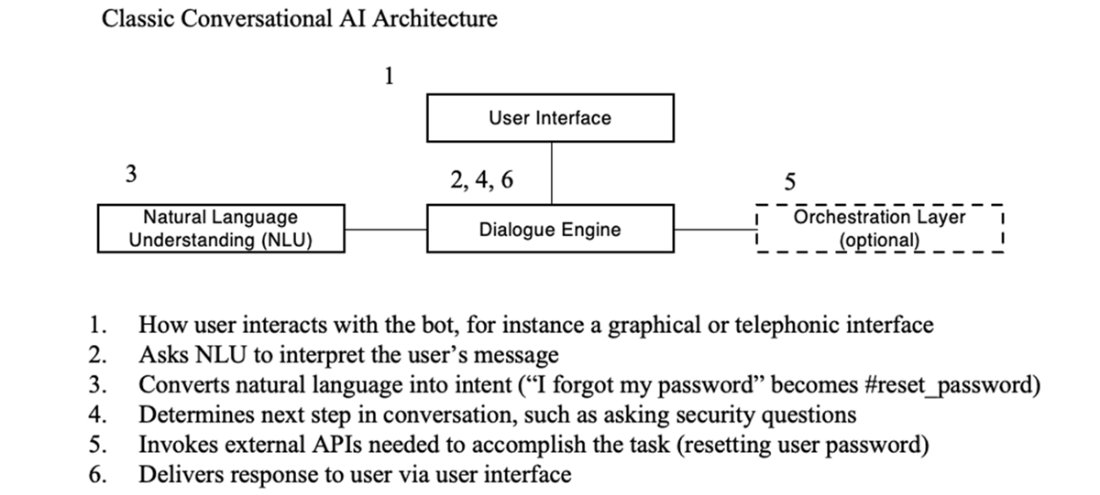
Conversational AI logical architecture annotated with password reset example.
It takes a dream team with diverse skills to build an enterprise-ready conversational AI.
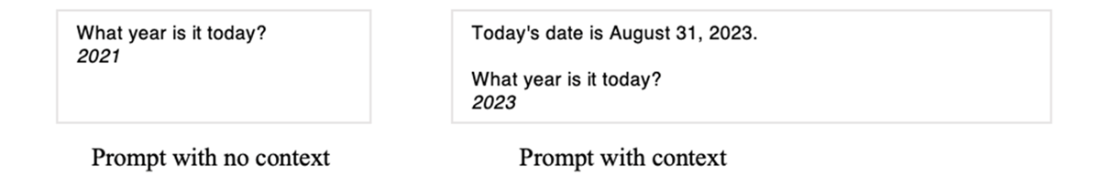
Adding context in the prompt is an important way to guide a large language model.
Impact of changing one LLM parameter (repetition penalty).

Cumulative success in a process is dependent on success in each of the individual steps. Visually it looks like a funnel that narrows after each step.
A continuous improvement lifecycle for conversational AI.
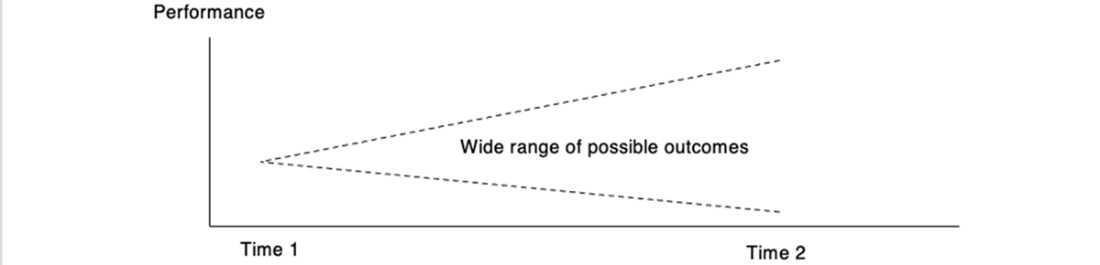
Large changes — like retraining all intents — take a long time and have less predictable outcomes.
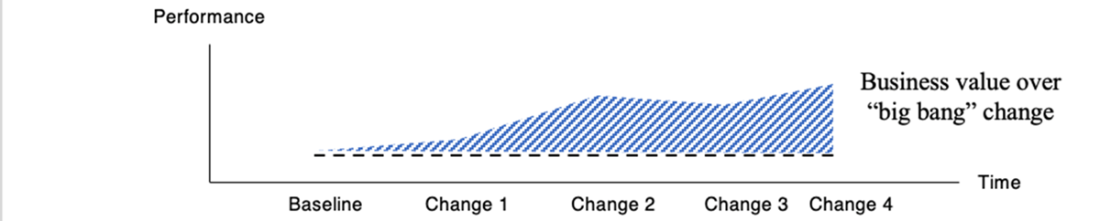
Many small changes — like retraining one intent at a time — has a smaller “blast zone” for each change, bringing quicker value and more learning.
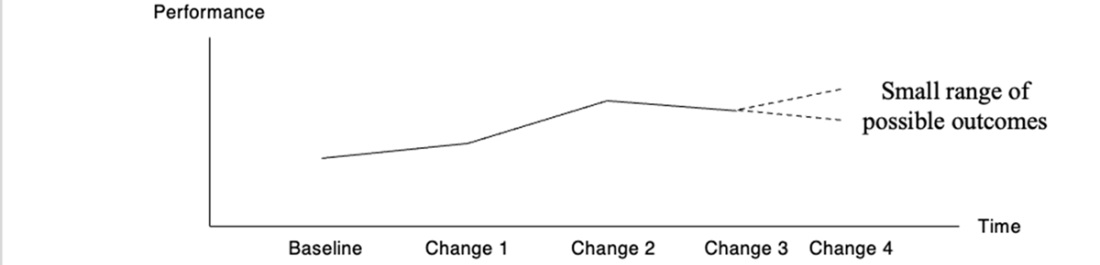
Area over the dotted line is additional business value over “big bang” change. Working code in production delivers value!
Summary
- Conversational AI must be built with the user experience in mind. Good conversational AI helps users complete their tasks quickly. Bad conversational AI frustrates users.
- There are thousands of generative AI models. Large language models are a subtype of generative AI models good at generating text.
- LLMs can perform many tasks with impressive performance but also have significant risks including hallucination. It takes thoughtful guidance and guardrails to use LLMs effectively and responsibly.
- LLM technology can supplement conversational AI. LLMs can respond to users directly and also assist you in building your conversational AI.
- Continuous improvement is possible and necessary for effective conversational AI.
- Iterative improvement delivers higher business value with lower risk.
 Effective Conversational AI ebook for free
Effective Conversational AI ebook for free