1 Introduction to Generative AI
This chapter introduces generative AI as a practical accelerator for software development, showing how context-aware assistants augment rather than replace developers. It outlines where these tools fit—from integrated IDE companions like code copilots to standalone chat-based systems—and positions them as catalysts for faster implementation, better tests, and clearer documentation without requiring AI expertise. The focus is on helping Python developers (and beyond) translate ideas into working software more quickly while shifting attention from boilerplate to architecture, design, and quality.
At the core are large language models powered by Transformer architectures and attention mechanisms that predict likely code given your inputs and surrounding context. Unlike traditional code completion driven by fixed rules, generative AI learns patterns from vast corpora and improves through a feedback loop of developer prompts, suggestions, and acceptance or edits. The chapter surveys common capabilities—code generation and autocompletion, bug detection and remediation, refactoring and optimization, test and mock data creation, and automated documentation—while contrasting probabilistic text prediction with deterministic systems to explain why results can be original, helpful, and occasionally wrong. It also clarifies how generative AI differs from classic code completion, and introduces emerging conversational “vibe coding” for rapid prototyping.
Because models can misinterpret context or inherit flaws from training data, the chapter stresses disciplined usage: provide precise specs and relevant code context, validate outputs, enforce quality gates, and apply prompt engineering and context management to improve accuracy. It presents an end-to-end workflow—ideation and planning, scaffolding and implementation, review and analysis, testing and debugging, and documentation—augmented by AI at each step. Practical adoption guidance covers tool selection, data and licensing considerations, integration with team processes and security, and keeping pace with fast-evolving capabilities. The takeaway is optimistic and grounded: used thoughtfully, generative AI amplifies human problem-solving, boosts productivity and software quality, and prepares developers for a future where design thinking and verification matter more than ever.
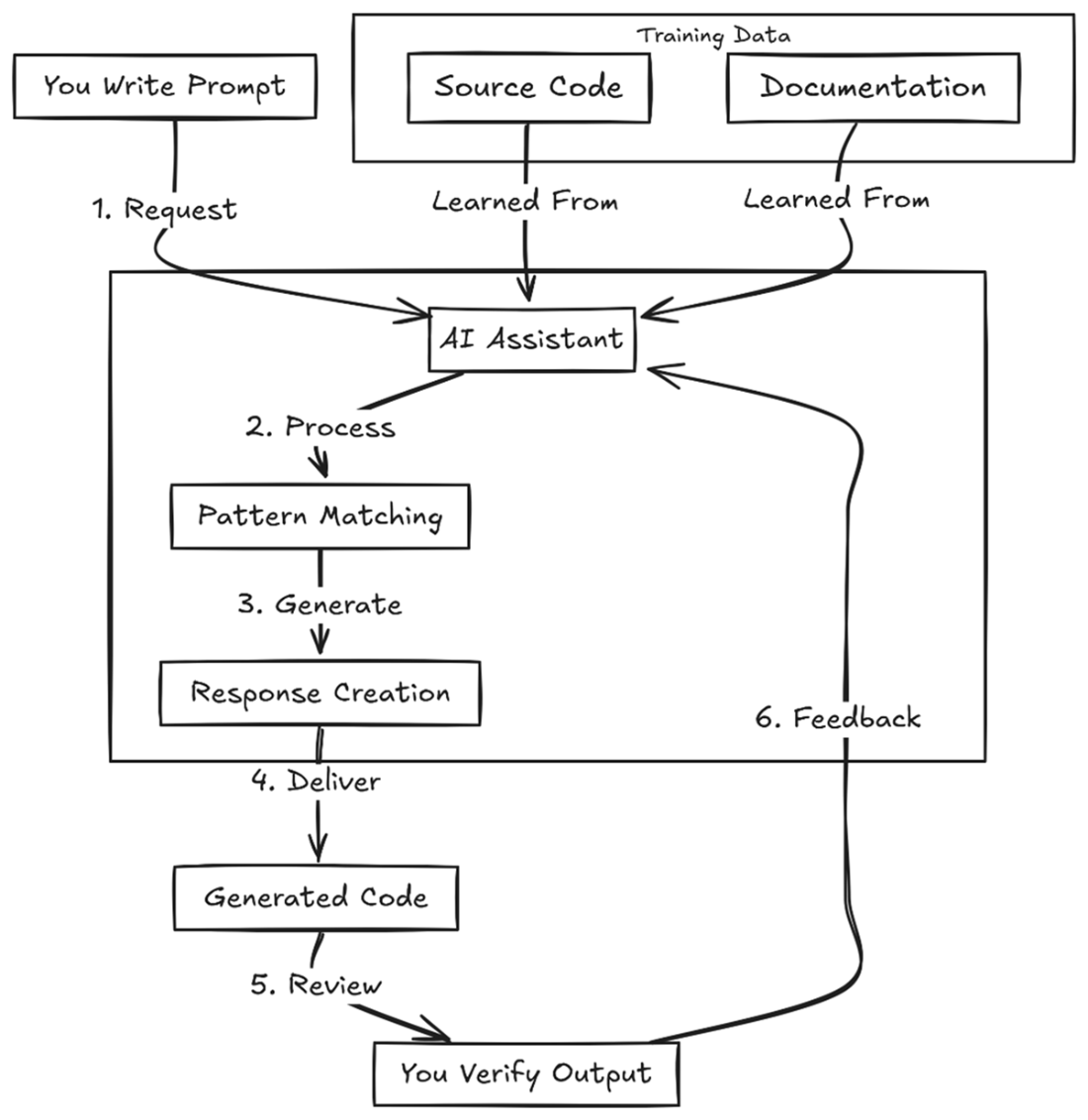
Integrated tools use a sophisticated system to generate code. It starts with your prompt, and the assistant gathers up documentation, and source code to see if your answer can come from these sources. It makes a best guess at what you’re looking for and generates a response. Your acceptance of these responses helps train the assistant in the future (unless you’ve blocked feedback).
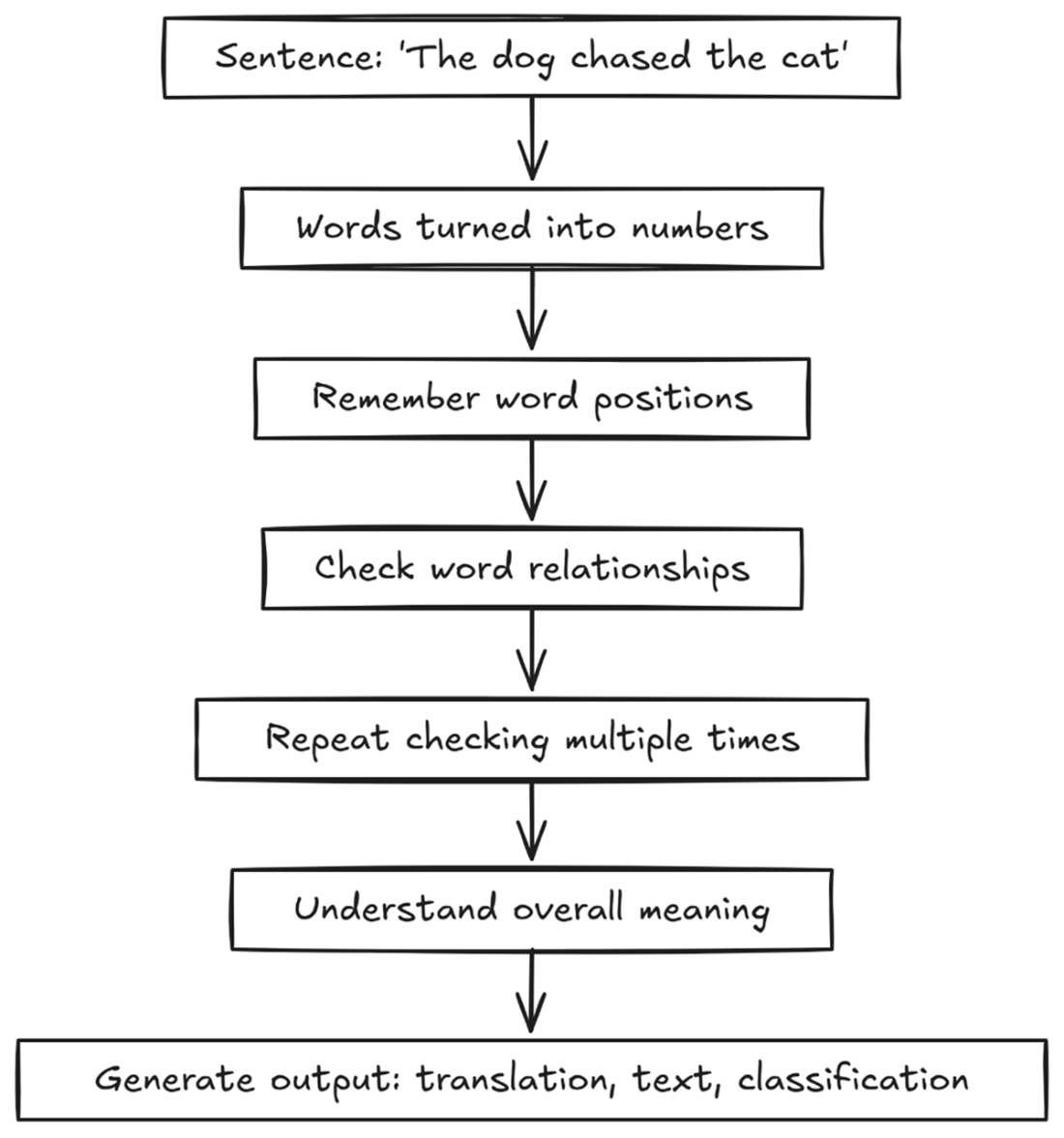
A transformer takes a sentence and analyzes word positions and relationships to try and extract meaning from the text it sees.
Mona Lisa riding a skateboard in the desert, courtesy of Midjourney

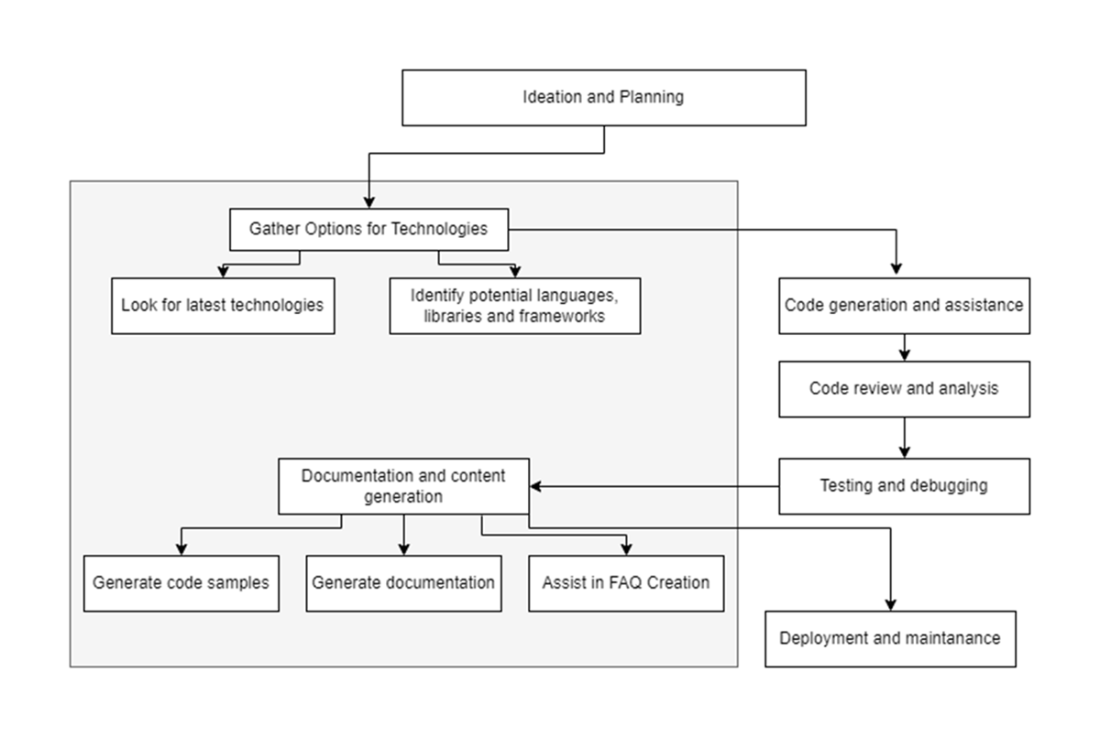
Generative AI tools play a big role in the planning process. From ideation and planning, to choosing a technology, to building the software and deploying it. Each of these steps can be enhanced with AI tooling.
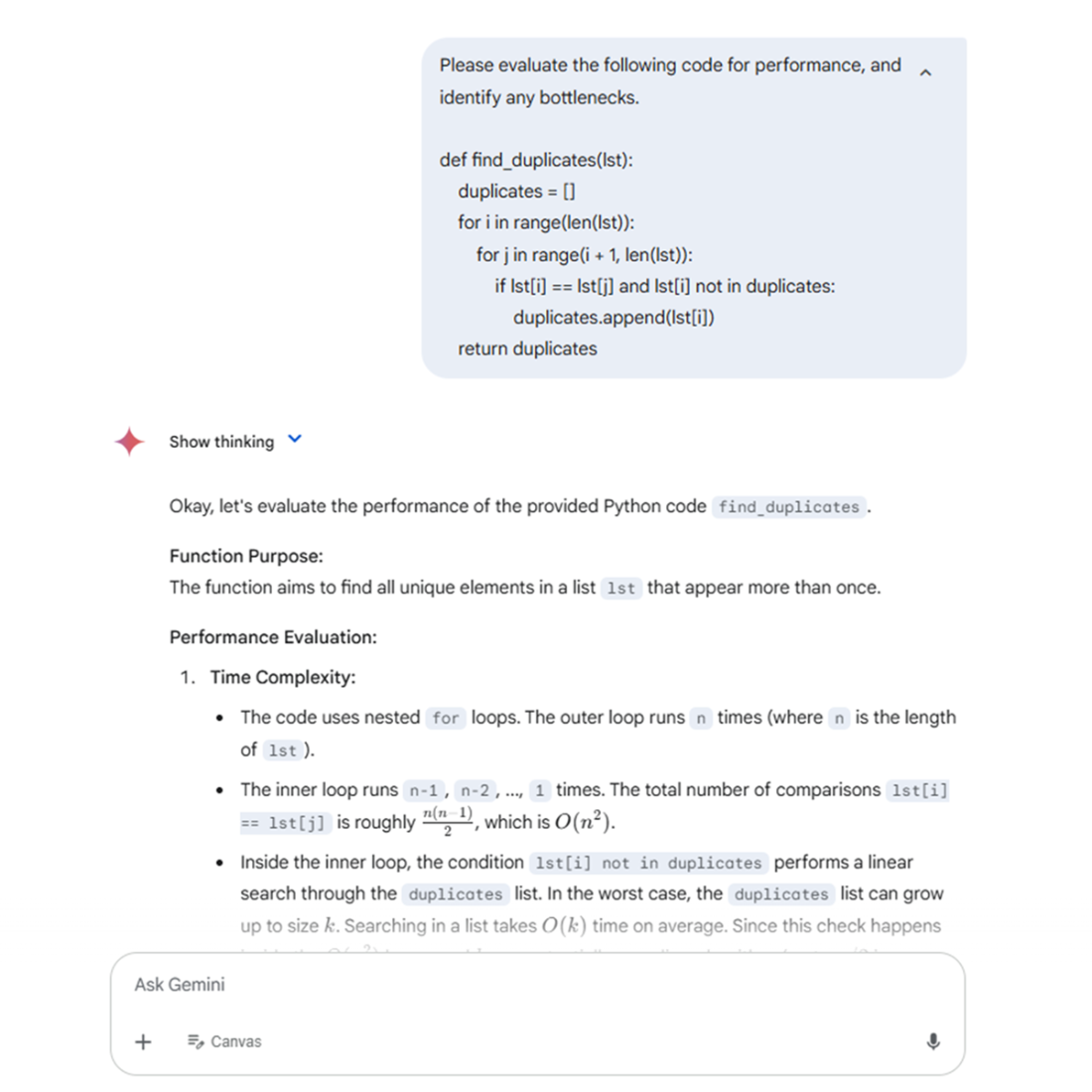
Even with a few lines of code Gemini can analyze it and make suggestions to improve it.
Summary
- Generative AI tools are changing software development. They boost productivity by generating code, finding bugs, and automating documentation.
- Modern AI tools come in two types: integrated tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine, which work in your IDE, and standalone solutions like ChatGPT and Gemini for bigger tasks.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) drive these tools. They learn patterns from huge code datasets, helping them create relevant code based on probabilities.
- It's important to know that AI tools make predictions, not certain outcomes. This understanding sets realistic expectations and shows why checking results is key.
- The AI-assisted development workflow includes ideation, planning, coding, testing, and documentation. Each phase gains unique benefits from AI support.
- To adopt AI tools effectively, consider training data quality, how they fit into workflows, quality assurance processes, and the need to adapt to new tools quickly.
- AI tools do not replace developers. Instead, they take care of routine tasks, letting humans focus on problem-solving, design, and creativity.
- As you read this book, you’ll discover ways to use these tools, making them valuable partners in your Python development process.
FAQ
What is generative AI and how does it help coders?
Generative AI uses large language models (LLMs) to understand your code and natural-language intent, then predicts and generates probable code, tests, and documentation. It accelerates tasks like autocompletion, scaffolding, refactoring, bug detection, and doc generation—often reducing implementation time while improving quality and coverage.
What’s the difference between integrated and standalone AI developer tools?
Integrated tools run inside your IDE (e.g., VS Code) and use your codebase as context to make inline suggestions while you type—great for implementation details. Standalone tools run in a separate web or app interface and excel at ideation, architecture, explanation, and broader discussions.
How do GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, and Blackbox AI compare?
- GitHub Copilot: IDE-integrated, context-aware completions and function suggestions, powered by OpenAI models (Codex lineage).
- Tabnine: IDE-integrated, context-aware suggestions with cloud and local options; “Deep Completion” aims for higher-accuracy, style-aware suggestions.
- Blackbox AI: Works in VS Code and Jupyter, supports 20+ languages, offers IDE chat and a web interface.
What is an LLM and how do Transformers generate code?
An LLM is a neural network trained on massive text/code corpora. Transformers use self-attention to analyze relationships across an entire sequence, learning patterns in language and code. Given a prompt, they predict the most likely next tokens to produce text or code. Outputs are probabilistic and tunable (e.g., temperature, top-k).
Why do AI coding tools sometimes produce incorrect or “hallucinated” results?
They generate by statistical prediction, not fact retrieval. Flaws can stem from imperfect training data, ambiguous prompts, or misread context. Mitigate by supplying clear specs and constraints, adding relevant code context, declaring inputs/outputs, specifying error handling, breaking tasks down, and always reviewing and testing outputs.
How are LLMs different from databases or search engines?
Databases and search retrieve stored information. LLMs generate new text by predicting likely continuations based on learned patterns. That’s why answers can vary across runs and may be confidently wrong—verification and testing are essential.
Where in the development workflow can AI help the most?
- Ideation and planning: architecture options, tech stacks, feature outlines.
- Code generation: scaffolding, inline suggestions, boilerplate.
- Code review: performance and security insights, refactoring ideas.
- Testing and debugging: unit tests, edge cases, error analysis.
- Documentation: API docs, explanations, user guides.
How is generative AI different from traditional code completion (e.g., IntelliSense)?
Traditional completion is rule/syntax-based with limited context. Generative AI learns from vast code corpora, models patterns and style, and can synthesize multi-line snippets or functions based on your current context and natural-language intent—more prescriptive and higher-level.
What should I consider when choosing and adopting AI tools?
Assess training data quality and licensing implications, security/privacy for proprietary code, integration with your IDE and team workflows, QA and review processes for AI-generated code, the pace of tool evolution, and the cultural shift toward architecture, validation, and oversight.
Will AI replace software developers?
No. It offloads repetitive boilerplate and accelerates implementation, but humans provide problem framing, domain knowledge, architectural judgment, ethics, and empathy. Expect a shift toward design, verification, and system thinking—using AI as a force multiplier, not a replacement.
 Coding with AI ebook for free
Coding with AI ebook for free