1 AI Reliability: Building LLMs for the Real World
AI has entered a new phase where large language models reason, plan, and act, powering tangible gains across industries from law and customer service to software development and enterprise automation. Yet most pilots still fail to deliver ROI because systems that impress in demos often break in production—hallucinations, brittle tool use, weak evaluations, and operational blind spots are common pitfalls. This chapter sets the stage for moving beyond flashy prototypes to durable, real-world systems and outlines a hands-on path to implement LLMs that remain accurate, reliable, and ethical over time.
A core theme is understanding and mitigating hallucinations—plausible but false outputs produced by probabilistic next-token generation over imperfect, contradictory training data. The chapter illustrates how convincingly fabricated content can surface in high-stakes domains (e.g., legal research) and defines reliability more broadly: truthfulness and grounding, consistency, graceful failure, fairness, efficiency, safe action-taking, and sustained quality as models and data evolve. Crucially, AI reliability adds semantic correctness to traditional software concerns like uptime and latency, since systems can be operationally healthy yet confidently wrong.
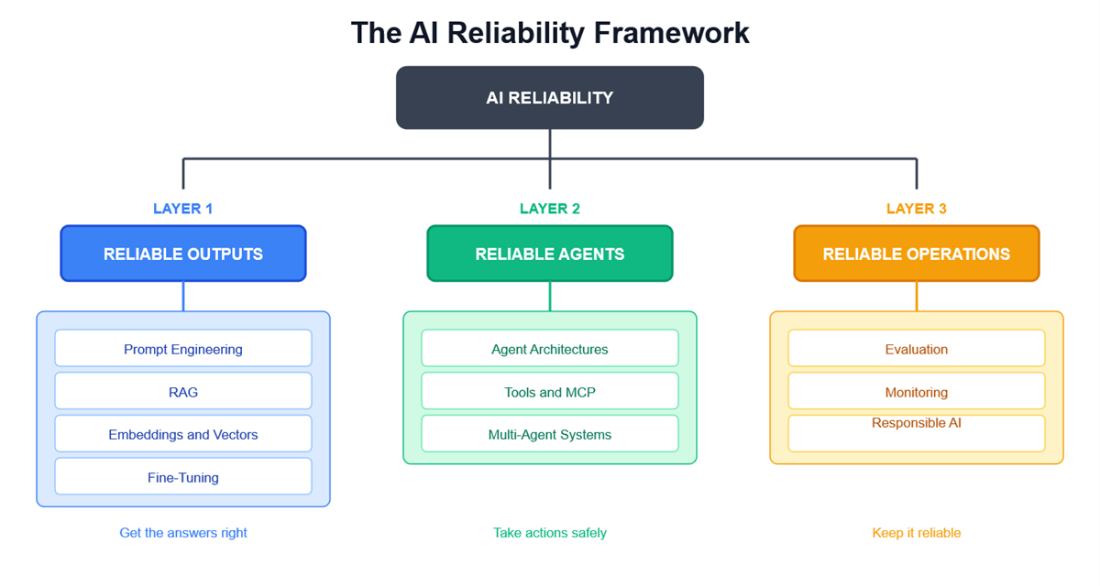
To operationalize reliability, the chapter introduces a three-layer framework and a practical toolbox. Layer 1 (reliable outputs) covers prompt engineering, RAG, embeddings/vector search, and fine-tuning to reduce hallucinations and ground responses. Layer 2 (reliable agents) addresses agent architectures, safe tool integration via MCP, and multi-agent coordination for complex workflows. Layer 3 (reliable operations) focuses on evaluation (including LLM-as-judge and red teaming), deployment, monitoring, and responsible AI practices around bias, privacy, and governance. The guiding principle is to start simple, add complexity deliberately, and measure from day one—an approach made urgent by real-world stakes, regulatory requirements, and the need to earn and keep user trust.
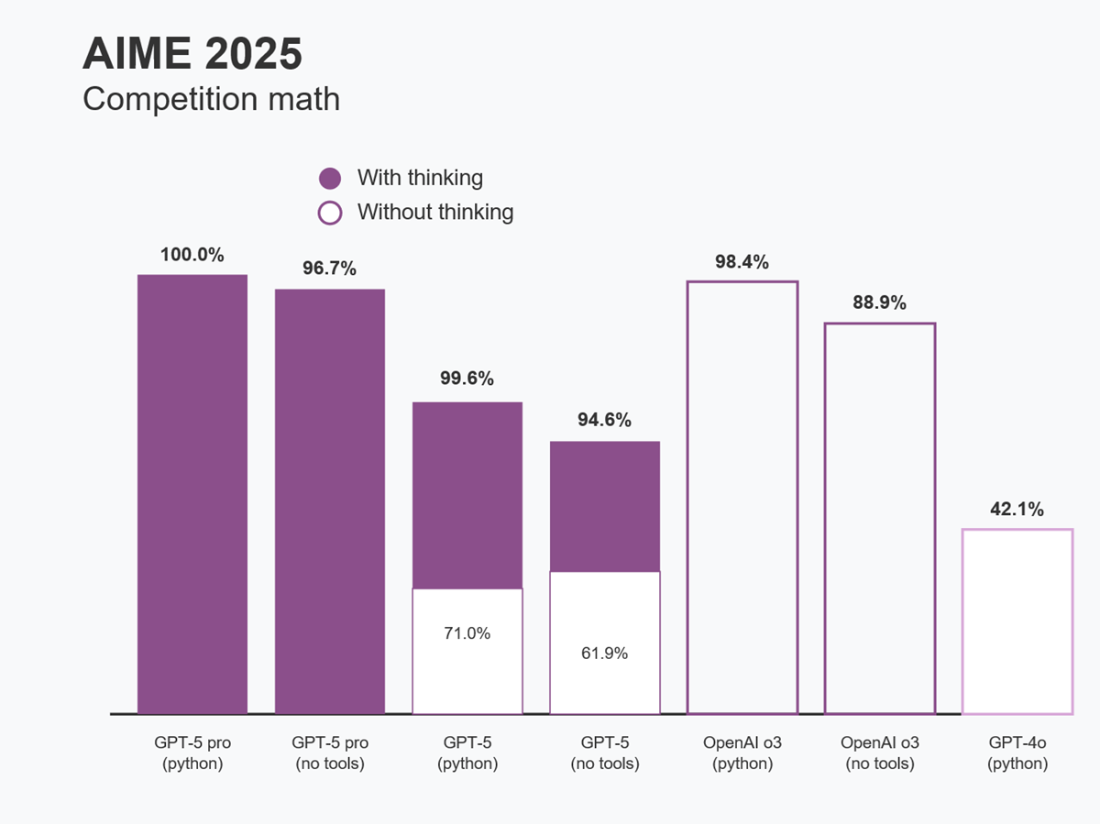
GPT model performance on AIME 2025 mathematics problems
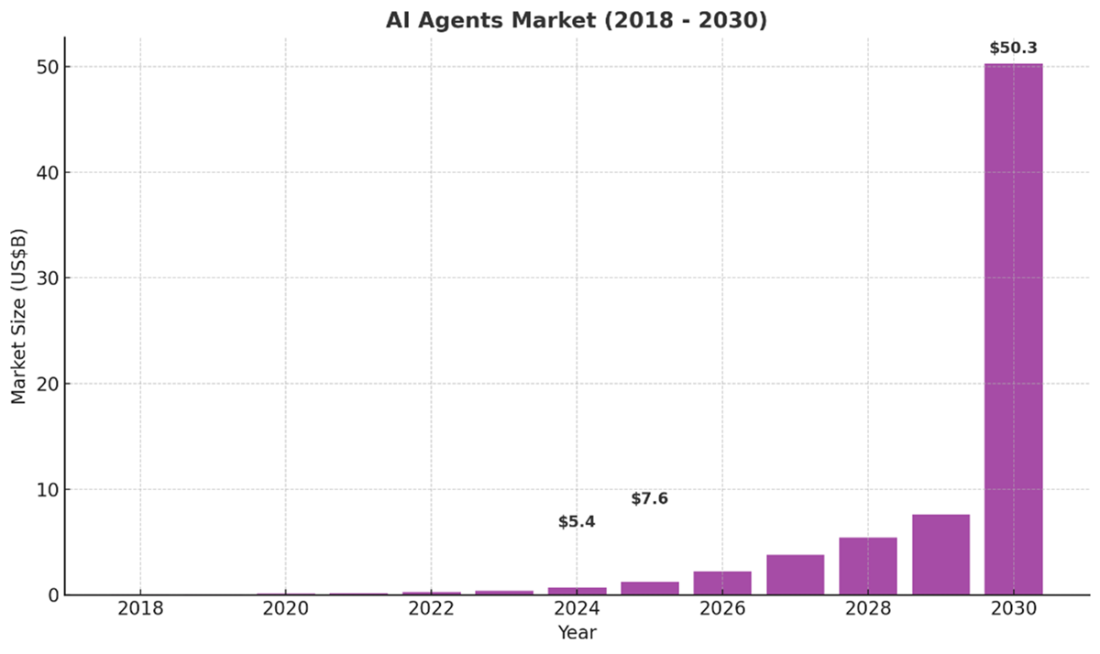
Global AI agents market forecast by region, 2018-2030
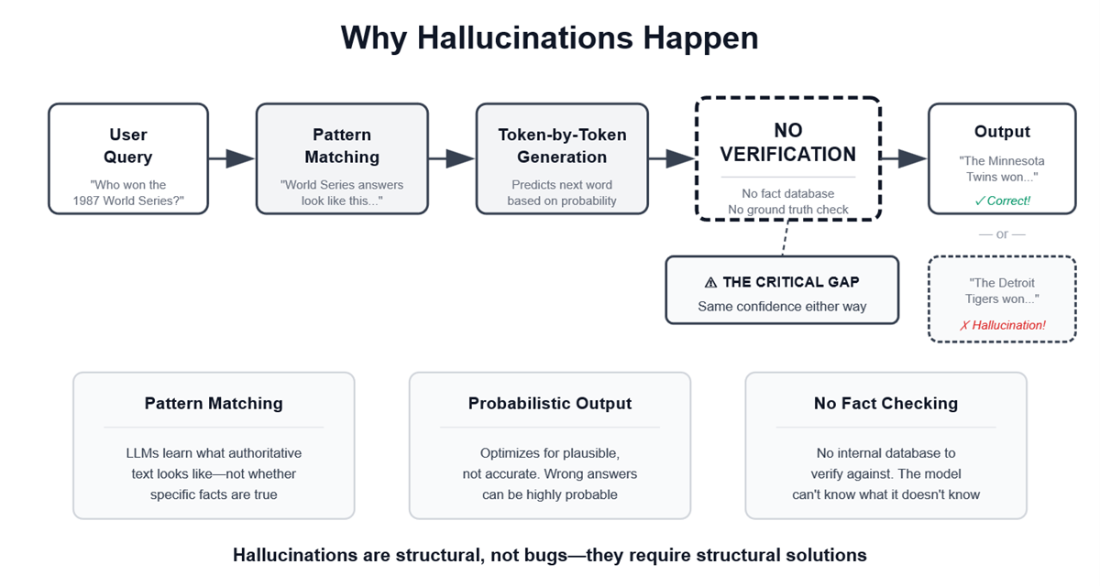
Why hallucinations happen from query to fabricated output
The AI Reliability Framework - three layers from outputs to operations
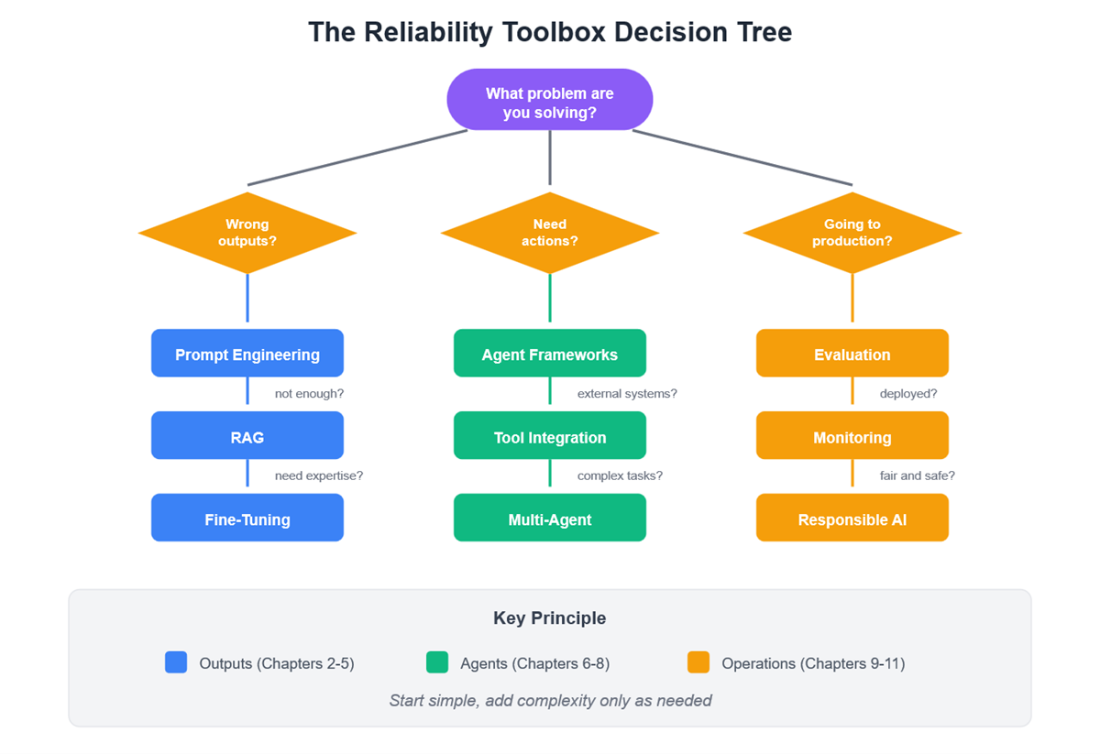
The Reliability Toolbox Decision Tree - choosing the right technique for your AI System
Summary
- LLMs have immense potential to transform industries. Their applications span content creation, customer service, healthcare, and more.
- Agentic AI systems that take real-world actions introduce new categories of risk requiring sophisticated reliability engineering.
- The three-layer framework organizes reliability: reliable outputs (Ch 2-5), reliable agents (Ch 6-8), reliable operations (Ch 9-11).
- Curbing hallucination risks is key to keep outputs honest and grounded in facts.
- Performance optimization ensures LLMs meet speed responsiveness demands, and quality of real-world applications.
- Multi-agent systems require coordination protocols, error handling, and monitoring to prevent cascading failures.
- The reliability toolbox includes prompt engineering, RAG, embeddings, fine-tuning, agent frameworks, tool integration, and evaluation - start simple, add complexity as needed but always build in evaluation and monitoring.
- This book covers promising solutions to these challenges that will enable safely harnessing LLMs to create groundbreaking innovations across healthcare, science, education, entertainment, and more while building vital public trust.
FAQ
What does “reliable AI” mean in this chapter?
A reliable AI system produces factual, grounded outputs; behaves consistently; fails gracefully (admits uncertainty rather than guessing); operates fairly without harmful bias; meets latency and cost targets; takes safe actions within defined bounds when granted agency; and maintains quality as models, data, and usage evolve. Beyond uptime and error rates, it emphasizes semantic correctness.
Why is reliability especially urgent now?
Reasoning-capable LLMs (e.g., GPT, Claude, Gemini “thinking” models) can plan, act, and coordinate complex tasks—raising the stakes of mistakes. While capabilities have surged (near-perfect scores on AIME-style problems, production-quality code, autonomous browsing), many pilots still fail to deliver ROI due to hallucinations, brittle tools, and weak evaluation. Reliability turns impressive demos into dependable systems.
What real-world benefits and risks do LLMs bring to industry?
- Law: JPMorgan’s COIN automates ~360,000 hours of contract review; risk: fabricated citations can cause legal damage.
- Customer service: Klarna’s assistant replaces work of ~700 agents, 2.3x faster in 35 languages, ~$40M/year savings; risk: incorrect policy info without guardrails.
- Development: GitHub Copilot boosts speed ~55%; risk: buggy/insecure suggestions require review.
- Enterprise AI: Salesforce Einstein → ~1B predictions/day, 25–35% revenue lift; risk: biased outputs in high-stakes contexts.
What is a hallucination, and why is it dangerous?
A hallucination is a confident but incorrect or unfaithful output. Unlike obvious software errors, hallucinations look plausible. Example: fabricated legal cases with realistic names and citations that fooled professionals—leading to sanctions and reputational harm.
Why do LLMs hallucinate?
- They generate text probabilistically to sound plausible, not to verify truth.
- Training data contains errors, gaps, and contradictions.
- No built-in fact-checking against ground truth at generation time.
- They learn the style of authoritative content (e.g., legal citations) without knowing if specific facts are true—so out-of-scope or conflicted queries can yield convincing fabrications.
What is the AI Reliability Framework introduced in this chapter?
- Layer 1: Reliable outputs (Ch. 2–5) — get accurate, grounded answers.
- Layer 2: Reliable agents (Ch. 6–8) — ensure safe, auditable tool use and actions.
- Layer 3: Reliable operations (Ch. 9–11) — evaluate, deploy, monitor, and keep systems reliable over time.
How do I get accurate, grounded outputs from an LLM?
- Prompt engineering: structured prompts, Chain-of-Thought, few-shot examples, and guardrails.
- RAG: retrieve relevant documents/data and require citations to reduce hallucinations.
- Embeddings and vector search: enable semantic retrieval when keywords fail.
- Fine-tuning (e.g., LoRA): bake domain expertise into the model when RAG and prompting aren’t enough.
How do I build agents that act reliably and safely?
- Architectures: use ReAct (reason-act loops), planning, and memory for auditable decisions.
- Tool integration: connect via Model Context Protocol (MCP) with permissions and boundaries.
- Multi-agent patterns: coordinate specialists with supervisor/oversight to avoid cascading failures.
- Guardrails: constrain actions, require confirmations, and log reasoning for review.
How should I evaluate, deploy, and monitor AI systems for reliability?
- Evaluation: reference metrics (ROUGE, BLEU), LLM-as-judge, red teaming, and human reviews.
- Observability: use platforms (e.g., Arize, Phoenix) to analyze real-world behavior.
- Operations: detect drift, alert on quality degradation, manage safe model updates, and close feedback loops.
- Track not just uptime/latency, but semantic quality, hallucination rates, and user satisfaction.
What’s in the “reliability toolbox,” and when should I use each tool?
- Prompt engineering — always start here; fastest gains.
- RAG — when outputs must be grounded in documents/data.
- Vector search — when keyword search isn’t enough.
- Fine-tuning — when deep domain expertise is required.
- Agent frameworks — for multi-step, decision-heavy tasks.
- Tool integration (MCP) — when the AI must act or access live data.
- Multi-agent systems — for complex workflows needing specialized skills.
- Evaluation and monitoring — always; you can’t improve what you don’t measure.
 Building Reliable AI Systems ebook for free
Building Reliable AI Systems ebook for free