1 The World of Large Language Models
This chapter introduces the rapid rise of large language models by first grounding the reader in the evolution of NLP: from early rule-based and statistical approaches to deep learning with neural networks that learn patterns at scale. LLMs are framed as next-word probabilistic predictors trained on vast, diverse corpora, enabling fluent dialogue, summarization, and reasoning that surpass the narrow, pre-scripted behavior of early voice assistants. The narrative emphasizes a practical, application-first lens—treating LLMs as building blocks in a broader ML ecosystem—while also noting the emerging frontier of multimodal models that integrate text with images and audio.
The chapter surveys where LLMs shine: conversational agents, text and code generation, information retrieval, language understanding tasks, recommendation, content creation and editing, and agentic task fulfillment. It outlines the ingredients and workflow behind LLM-powered apps—defining the use case, securing compute, training and fine-tuning—then highlights the role of scale: massive datasets (e.g., web-scale crawls), distributed training on GPUs/TPUs, and cost models tied to tokens. A focal example is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which retrieves relevant context from a targeted corpus and fuses it into generation to improve accuracy and topical freshness, while acknowledging that reliability depends on the quality and scope of the underlying knowledge base.
Balancing promise with realism, the chapter details key limitations—bias, ethical risks, opacity in decision-making, and hallucinations—underscoring the need for safeguards, validation, and responsible deployment. It closes with a tour of the startup ecosystem catalyzed by LLMs: lightweight “wrapper” apps, infrastructure players building vector databases and orchestration frameworks, and capital-intensive model developers competing at the frontier with massive GPU fleets. The book’s scope centers on building effective LLM applications—practical patterns, tooling, and deployment—setting the stage for a deeper look at the architectures that make these systems so capable.
An output for a given prompt using ChatGPT
Rose Goldberg’s famous self-operation napkin constructing an LLM application demands a thoughtful orchestration of resources, from computational power to application definition, echoing the complexity of Rube Goldberg's contraptions.
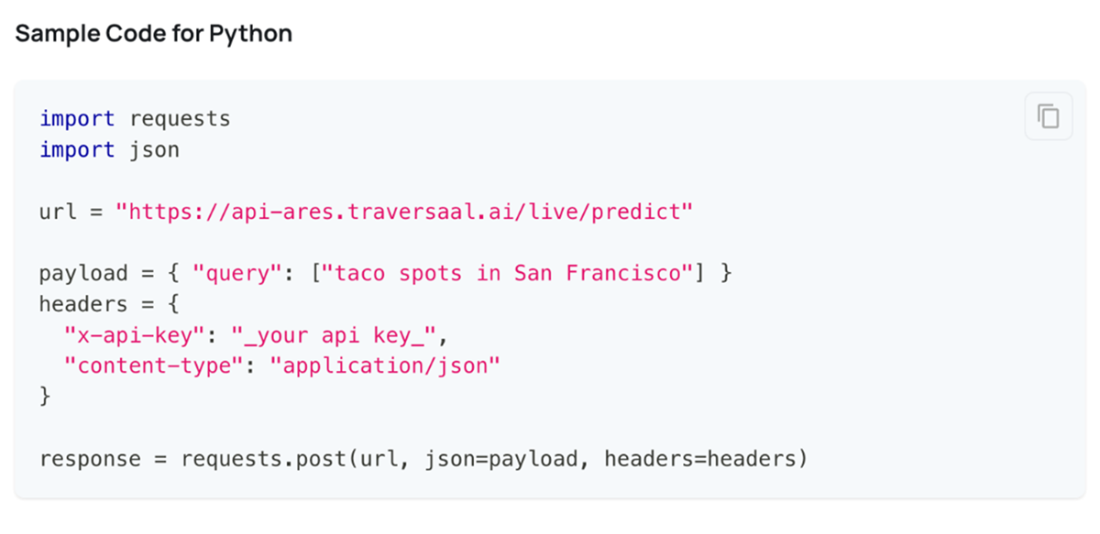
A Python code snippet demonstrating how to use the Ares API to retrieve information about taco spots in San Francisco using the internet. Instead of just showing URLs, the API returns actual answers with web URLs as source
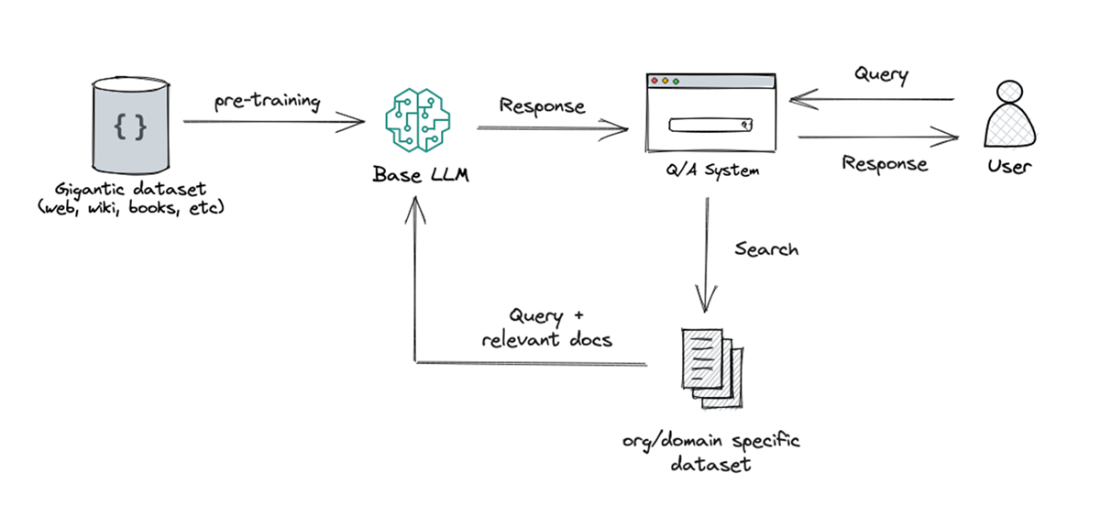
Retrieval Augmentation Generation is used to enhance the capabilities of LLMs, especially in generating relevant and contextually appropriate responses. The approach involves incorporating an initial retrieval step before generating a response to leverage information from a knowledge base.
Summary
- Large language models (LLMs) are the latest breakthrough in natural language processing after statistical models and deep learning. LLMs stand on the shoulders of this prior research but take language understanding to new heights through scale.
- Pretrained on massive text corpora, LLMs like GPT-3 capture broad knowledge about language in their model parameters. This allows them to achieve state-of-the-art performance on language tasks.
- Applications powered by LLMs include text generation, classification, translation, and semantic search to name a few.
- LLMs utilize multi-billion parameter Transformer architectures. Training such gigantic models requires massive computational resources only recently made possible through advances in AI hardware.
- Bias and safety are key challenges with large models. Extensive testing is required to prevent unintended model behavior across diverse demographics.
- Numerous startups are offering LLM model APIs, democratizing access and allowing innovation in the realm of Generative AI.
FAQ
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
An LLM is an AI system trained on massive text datasets to predict the next word (token) in context. At scale, this probabilistic next-word prediction captures patterns of grammar, semantics, and discourse, enabling the model to generate coherent, contextually relevant, human-like text. “Large” refers to both the volume of data and the number of parameters used during training.How did NLP evolve into today’s LLMs?
NLP began with early rule-based and statistical methods (e.g., simple translation systems in the 1940s). With the internet’s explosion and advances in deep learning, multi-layer neural networks learned complex language patterns from vast datasets. Early assistants like Siri and Alexa offered narrow, predefined capabilities; modern LLMs leverage greater compute and data to craft paragraphs, hold rich conversations, and generalize across topics.What does it take to build an LLM application?
Successful apps require: defining the use case and evaluation goals; securing adequate compute (typically GPUs) and choosing the right model; assembling data pipelines for training, fine-tuning, or retrieval; integrating techniques like RAG for up-to-date or domain-grounded answers; orchestrating prompts, tools, and workflows; and deploying/monitoring for quality, cost, and reliability. The pieces must be thoughtfully coordinated.How are LLMs trained and fine-tuned?
Training exposes a model to huge corpora (e.g., Common Crawl) to learn to predict the next token by iteratively adjusting weights and biases. This is compute-intensive and often runs on distributed GPUs/TPUs for weeks. Fine-tuning adapts a pre-trained model to a specific domain or task (e.g., legal, medical) with targeted data, improving performance without retraining from scratch. Providers typically recover costs via per-token API pricing or subscriptions.Why do LLMs need vast datasets?
- Learn general language patterns usable across contexts
- Capture rich semantics from diverse topics and styles
- Develop strong contextual awareness for coherent responses
- Improve robustness and adaptability to varied inputs
- Handle ambiguity by learning disambiguating cues
- Avoid overfitting and generalize to unseen data
What are the main applications of LLMs?
- Conversational assistants and chatbots (often with retrieval augmentation)
- Text and code generation: drafting, translation, summarization, creative writing
- Information retrieval and organization: better query understanding and ranking
- Language understanding: sentiment, intent, NER, tutoring
- Recommendation systems: personalized suggestions and adaptation
- Content creation and editing: style, clarity, grammar, restructuring
- Agent-based task fulfillment: multi-step actions via tools and services
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and how does it work?
RAG improves answers by grounding generation in external knowledge. It searches a curated corpus (not the whole internet) for relevant passages, integrates them with the user’s query, and then generates a response. Typical flow:- Retrieval: find relevant documents/snippets
- Candidate selection: prepare useful context
- Context integration: combine retrieved info with the prompt
- Response generation: produce an answer grounded in the retrieved evidence
What are multimodal models and how do they differ from text-only LLMs?
Multimodal models jointly process multiple data types—text, images, audio, etc. Unlike text-only LLMs, they can interpret an image or audio clip and produce relevant text, or combine modalities for tasks like visual question answering and mixed-media content creation. This more closely mirrors human perception. An example highlighted in the chapter is Google’s Gemini.What challenges and limitations do LLMs face?
- Data bias: training data can encode stereotypes and unfairness
- Ethical risks: potential for misleading, harmful, or unsafe content
- Interpretability: models act as “black boxes,” complicating trust
- Hallucinations: confident but incorrect or nonsensical outputs
 Build an LLM Application (from Scratch) ebook for free
Build an LLM Application (from Scratch) ebook for free