1 Using generative AI in web apps
Generative AI web apps integrate advanced models—especially large language models—to produce text, images, audio, and video on demand, enabling personalized, adaptive experiences and new product categories. This chapter explains what these apps can do and how to build them for production: integrating models from providers such as OpenAI and Google AI, developing with React and Next.js, and using the Vercel AI SDK for clean state management and provider abstractions. It assumes basic JavaScript and React knowledge, introduces the Model Context Protocol for secure access to tools and data, and sets up hands-on learning that culminates in a voice-driven interview assistant and a RAG-powered corporate knowledge system.
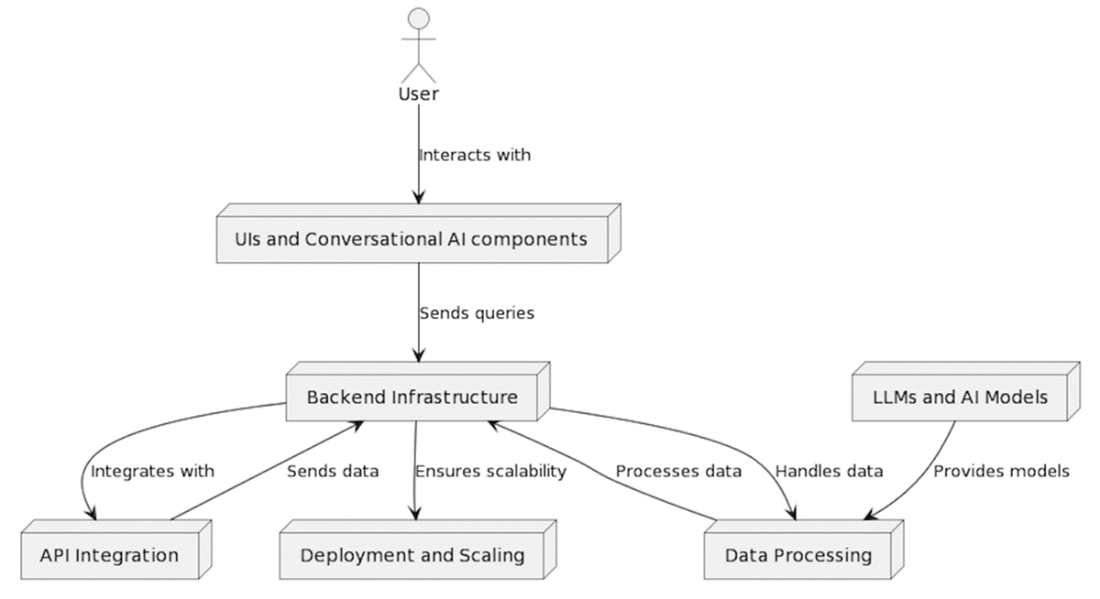
Under the hood, these apps orchestrate UIs and conversational components with backends that enforce safety, privacy, and reliability while brokering calls to LLMs and other services. Infrastructure typically combines caching, serverless functions, container orchestration, and model-serving frameworks with data pipelines for pre- and post-processing. A common interaction flow moves from user input through preprocessing and model selection to generation and response delivery, often with a feedback loop. Real-world opportunities include marketing content and imagery, customer-support chatbots with sentiment-aware replies, and mock interview agents that blend speech-to-text, adaptive scenarios, and real-time feedback.
Generative AI goes beyond traditional classification to create new content, powered by transformer architectures and self-attention that capture long-range context. Selecting the right approach involves matching tasks to model families (for example, autoregressive LLMs for text, GANs and VAEs for images), weighing pre-trained APIs against self-hosted options, and planning for latency, throughput, and pre/post-processing within the user experience. The chapter also emphasizes responsible use: validating outputs to reduce hallucinations, auditing for bias, complying with privacy and intellectual property requirements, and delivering accessible, high-quality interfaces—positioning developers to automate routine work while focusing on higher-value creativity.
The flow of information and interactions between the key components of a generative AI web application.
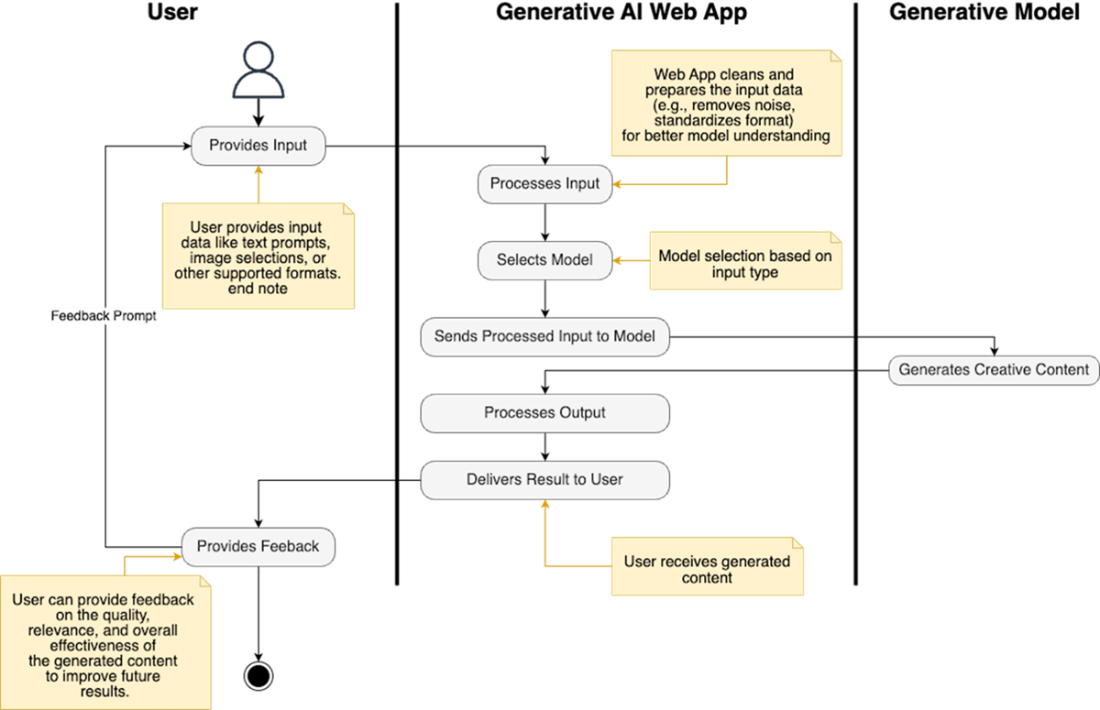
How an AI web app works: users input data, the app processes it, selects a model, generates content, delivers it, and optionally collects feedback.
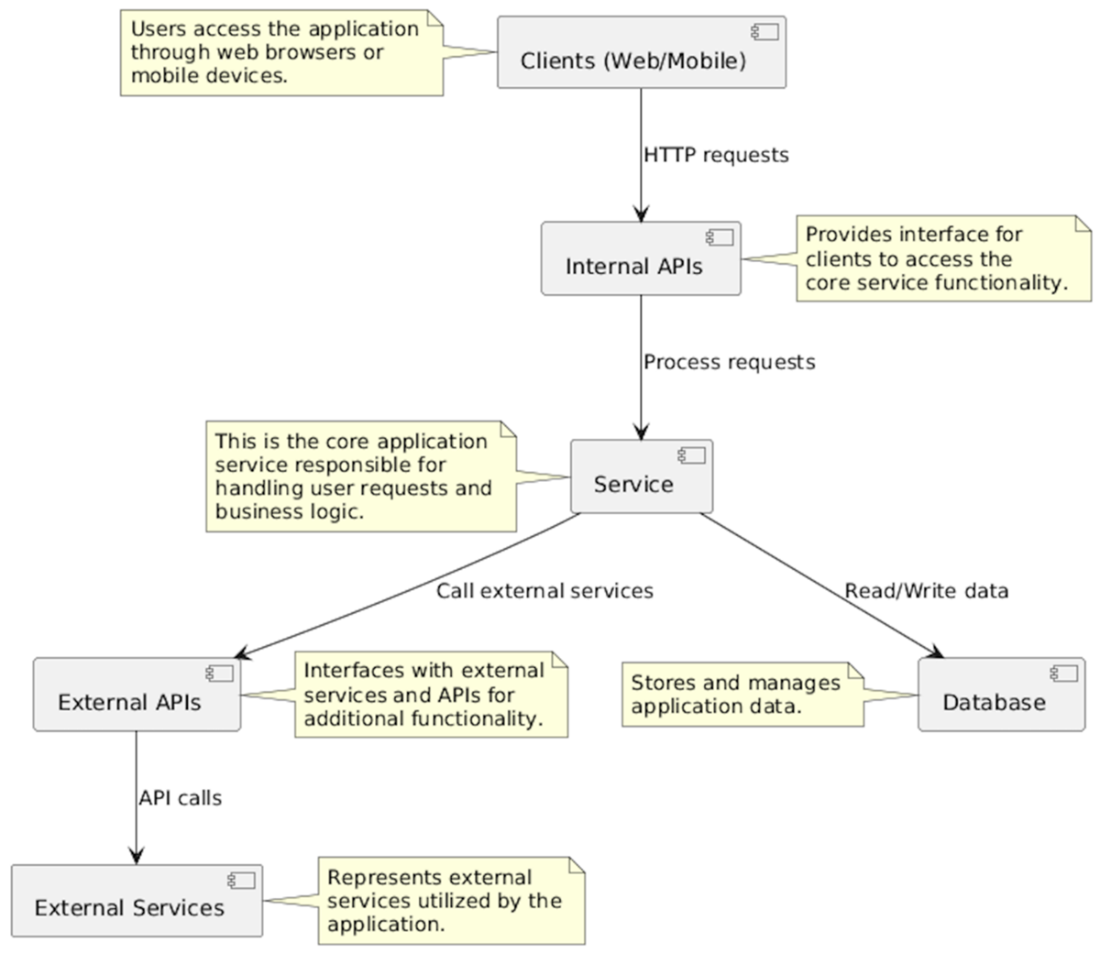
Simplified architecture diagram of a web application ecosystem. Clients, including web browsers and mobile devices, interact with the core application service, which handles user requests and business logic. The service interacts with a database to store and manage application data. Additionally, the service communicates with external APIs to access additional functionality and interacts with external services utilized by the application.
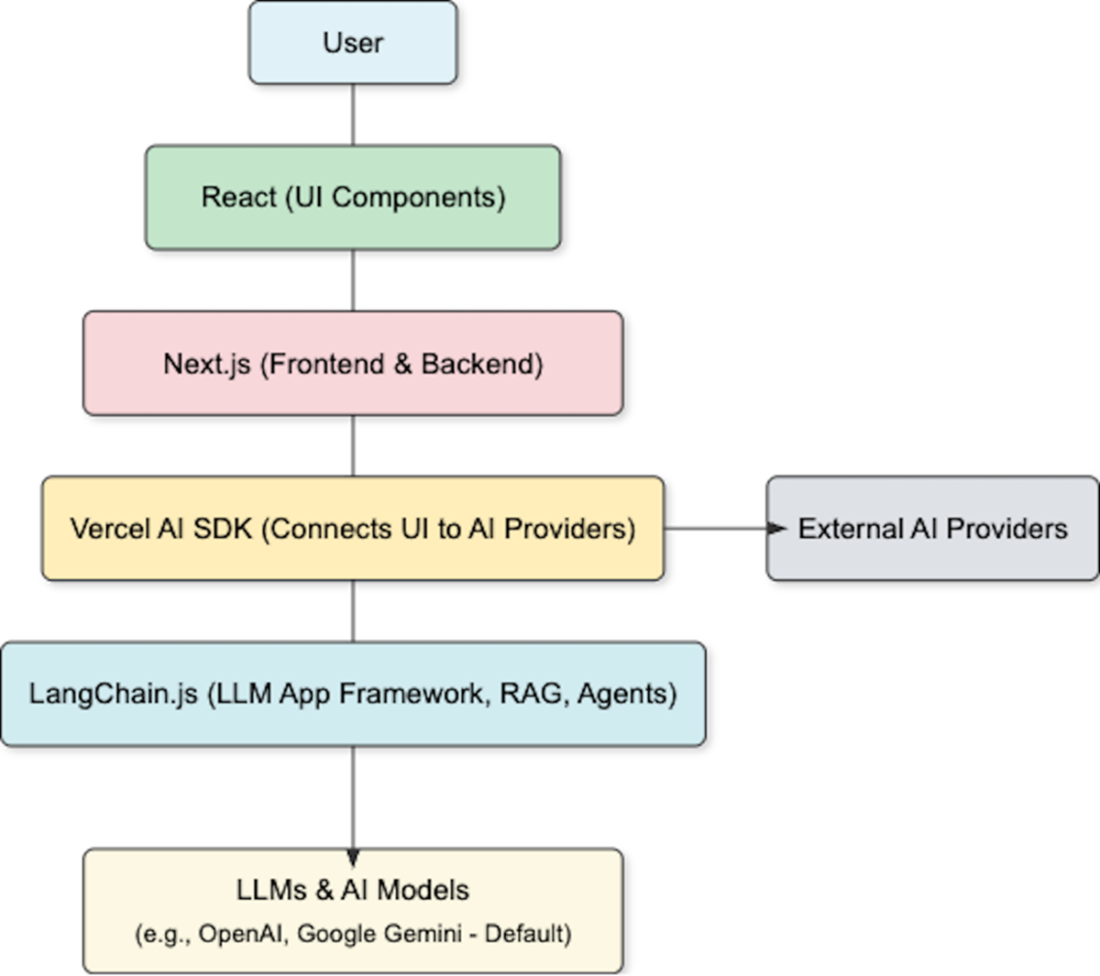
Leveraging key technologies to create generative AI web applications
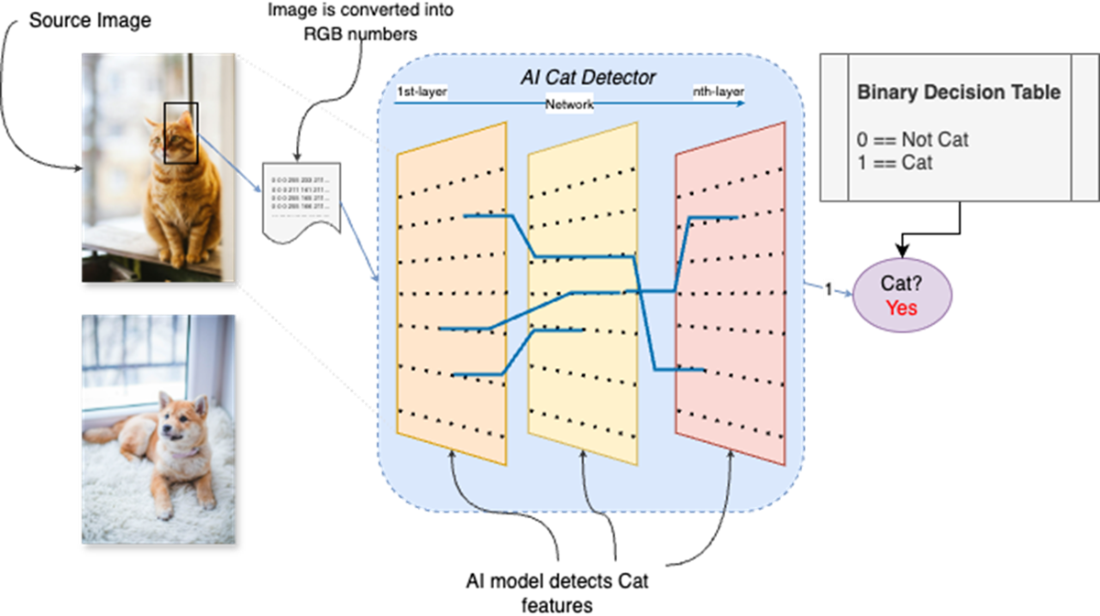
How AI can be used to detect whether a picture of a cat is a cat or not. It accepts an image as input and responds with yes or no (or 0 and 1).
Summary
- Generative AI can generate not only text, but all sorts of media resources like images, video clips and audio. This greatly enhances their potential usage in web applications, and real-world uses of generative AI in web applications range from digital marketing and customer experience management to mock interview applications.
- Generative AI web apps center on powerful models like large language models (LLMs) to create content from user input. The apps require a full supporting ecosystem to integrate with the model, including UI and conversational AI components, backend infrastructure, data processing pipelines, API integration, and deployment and scaling mechanisms.
- The apps we build in this book will use JavaScript and React to display the UI interface components, along with Next.js and the Vercel AI SDK to manage the backend and interact with external AI service providers.
- Choosing the right model for an app is a key architectural decision and depends on the task required. Different model types ( such as LLMs, GANs, autoregressive, transformers, VAE, and RNNs) excel at different kinds of problems. But the model architecture is just one consideration; developers also need to consider the quality and type of data it was trained on.
- Software engineers have been using AI long before generative AI came into existence. Common applications include machine learning, search recommendations, chatbots and computer vision.
- Foundational research like Google's "Attention is All You Need" laid the groundwork for transformative technologies such as transformers, which simplified natural language processing tasks by leveraging attention mechanisms. Transformers revolutionized language modeling by improving efficiency and accuracy in understanding textual data, addressing long-standing challenges faced by traditional AI models.
- Limitations of generative AI include quality control issues, resource intensiveness, security concerns, and regulatory compliance. Concerns include its potential impact on jobs, the reliability of outputs, handling bias, and enhancing the user experience.
 Build AI into Your Web Apps ebook for free
Build AI into Your Web Apps ebook for free