1 Introduction to DeepSeek
Large language models have reshaped how we interact with technology, and this chapter invites you to go beyond using them to actually build one. It frames DeepSeek as a watershed in open-source AI—an openly available model that rivals closed, proprietary systems—and sets the tone for a hands-on journey where theory and code advance together. The chapter introduces the goals of the book, explains why DeepSeek is the ideal case study, and previews the path you will take to understand and implement its most important ideas.
At the core of DeepSeek’s leap are four technical pillars: Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) to relieve attention’s speed and memory bottlenecks, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layer to expand capacity efficiently, Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) to accelerate learning and inference, and FP8 quantization to push compute and memory efficiency. These are complemented by an optimized training pipeline that overlaps tasks to maximize hardware utilization and a post-training recipe that layers reinforcement learning, rejection sampling, and fine-tuning to instill strong reasoning skills. The chapter also highlights DeepSeek-R1’s headline results—top-tier benchmark performance at markedly lower training cost—and the team’s commitment to democratization through open weights and distilled checkpoints from small (1.5B) to large (70B) models.
The book is organized into four stages: foundational inference mechanics (including the KV cache), architectural advances (MLA and MoE), training efficiency (MTP, FP8, and pipeline scheduling), and post-training methods (supervised fine-tuning, RL, and distillation). You will learn to reason from first principles and implement each component, but the scope stops short of reproducing proprietary data, training trillion-token corpora, or production-scale serving. To follow along, you should be comfortable with Python, basic deep learning and PyTorch, and have a general grasp of transformers; a CPU is sufficient for most exercises, while a single consumer GPU (8–12 GB VRAM) makes experimentation smoother. Overall, the chapter sets expectations, tools, and mindset for building a mini-DeepSeek and understanding modern LLM design end to end.
A simple interaction with the DeepSeek chat interface.

The title and abstract of the DeepSeek-R1 research paper.

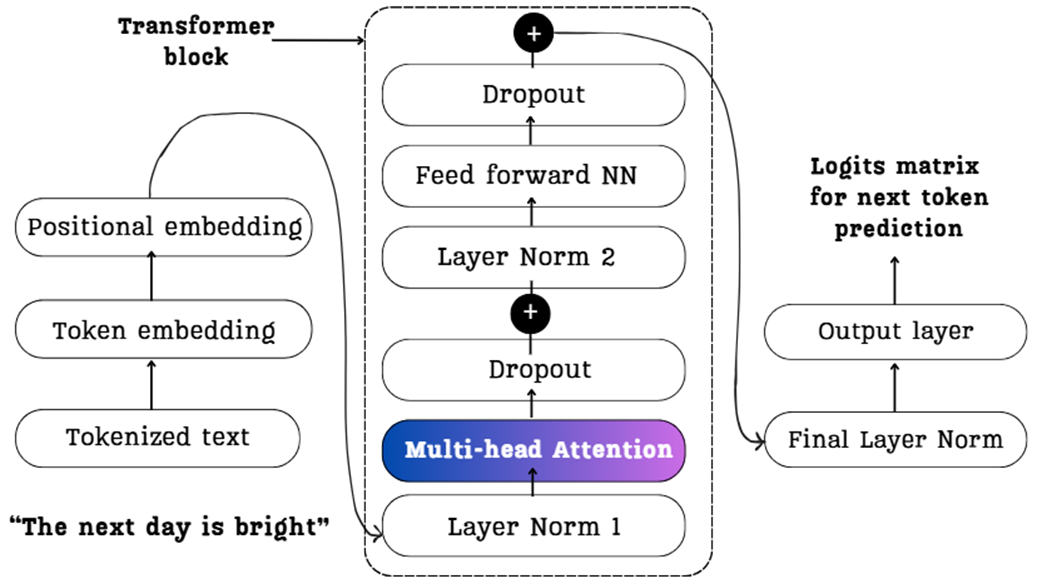
A detailed view of a standard Transformer block, the foundational architecture used in models like LLaMA and the GPT series. It is composed of a multi-head attention block and a feed-forward network (NN).
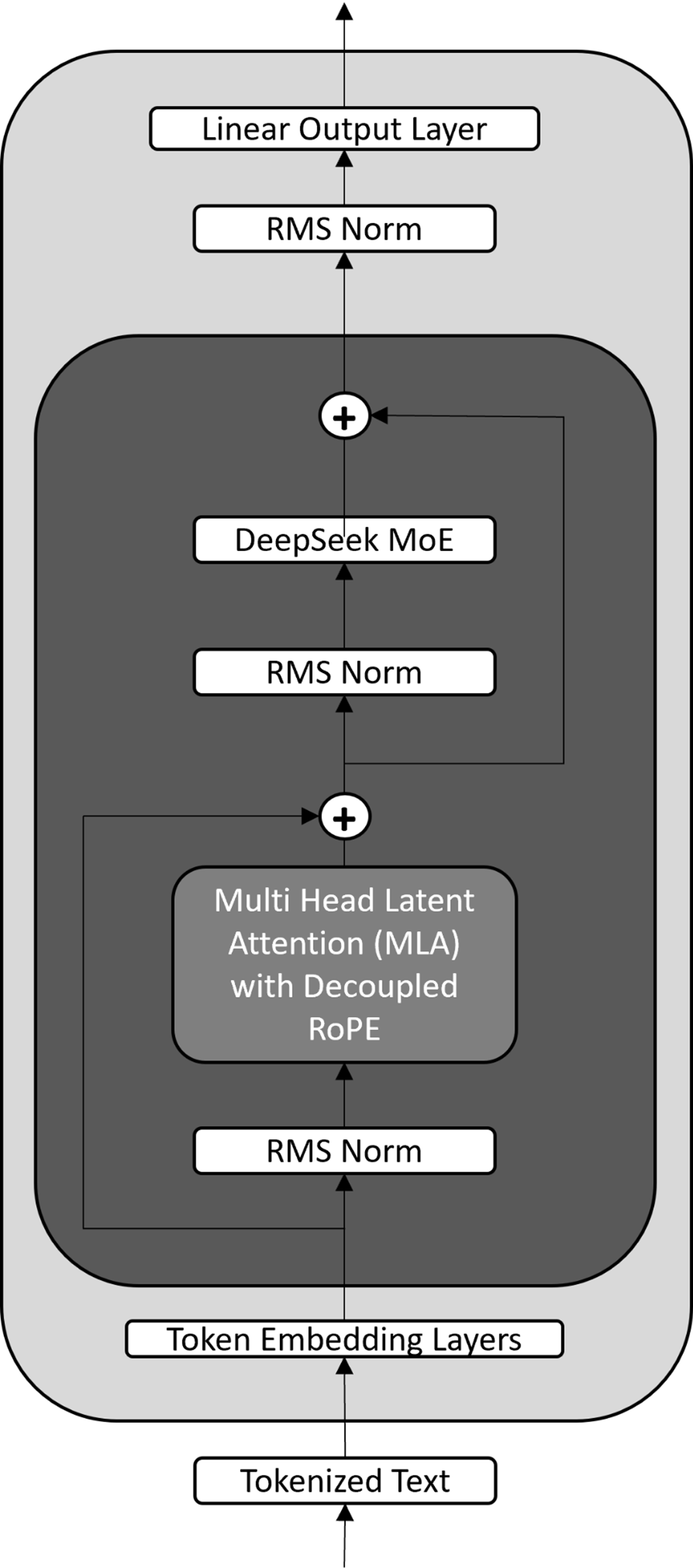
A simplified view of the DeepSeek model architecture. It modifies the standard Transformer by replacing the core components with Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layer. This design also utilizes RMS Norm (Root Mean Square Normalization) and a specialized Decoupled RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding).
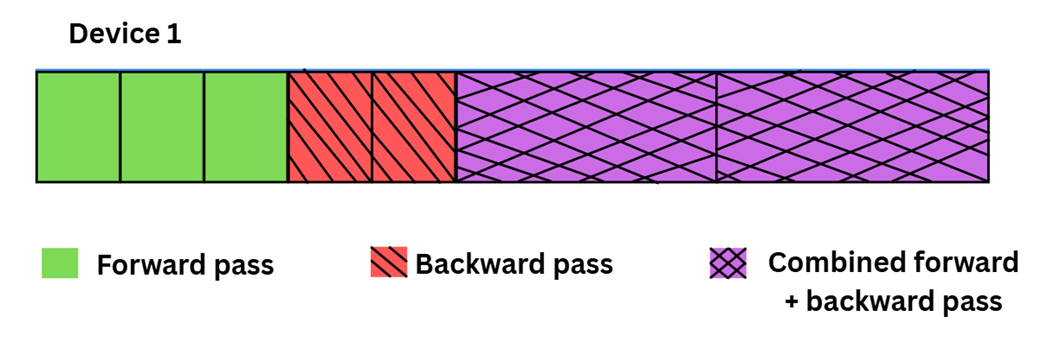
An illustration of the DualPipe training pipeline on a single device. By overlapping the forward pass (the initial blocks), backward pass (the hatched blocks), and combined computations, this scheduling strategy minimizes GPU idle time and maximizes hardware utilization during large-scale training.
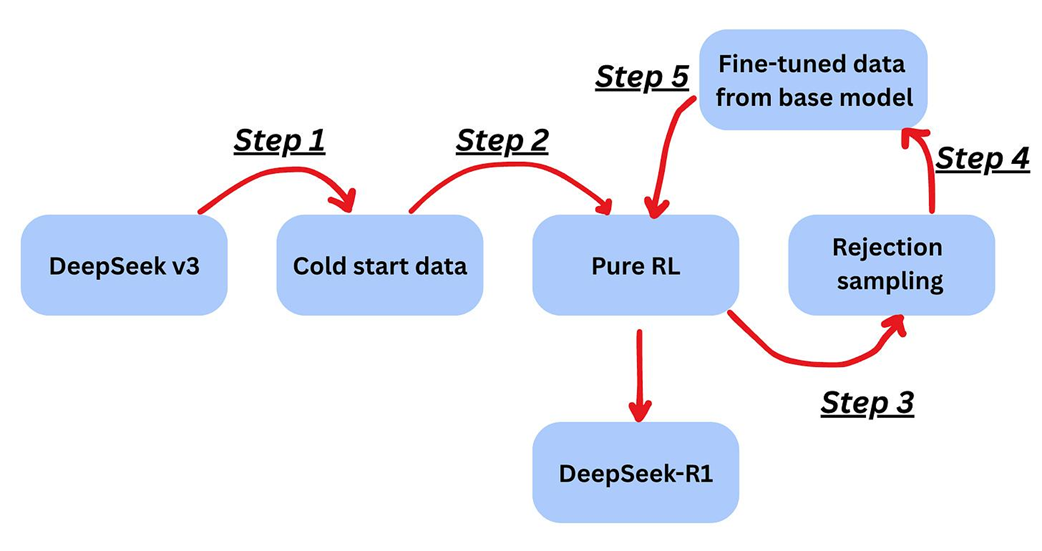
The multi-step post-training pipeline used to create DeepSeek-R1 from the DeepSeek-V3 base model. This process involves a combination of reinforcement learning (Pure RL), data generation (Rejection sampling), and fine-tuning to instill advanced reasoning capabilities.
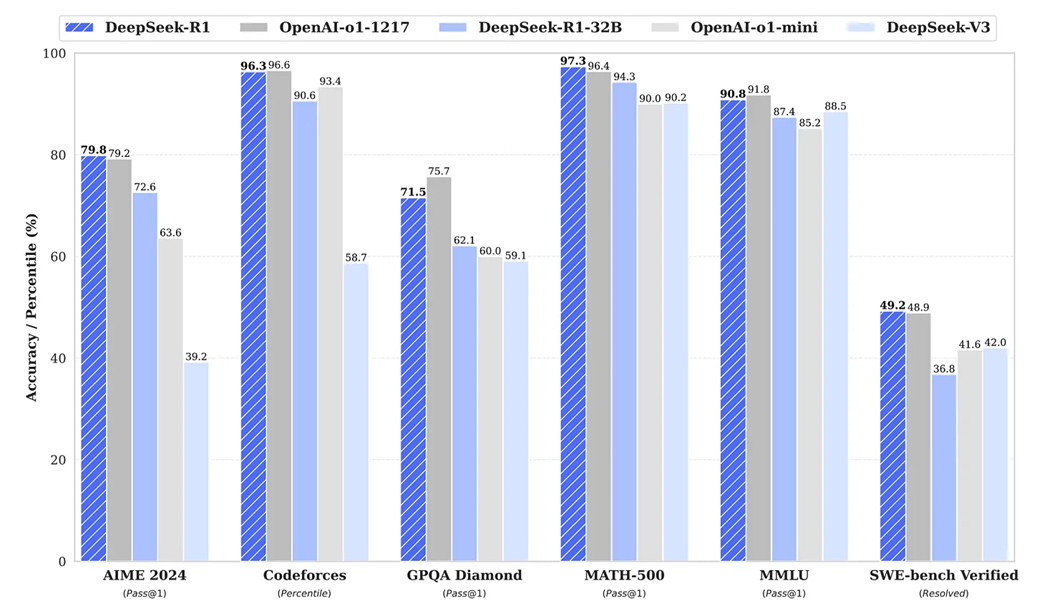
Benchmark performance of DeepSeek-R1 against other leading models (as of January 2025).
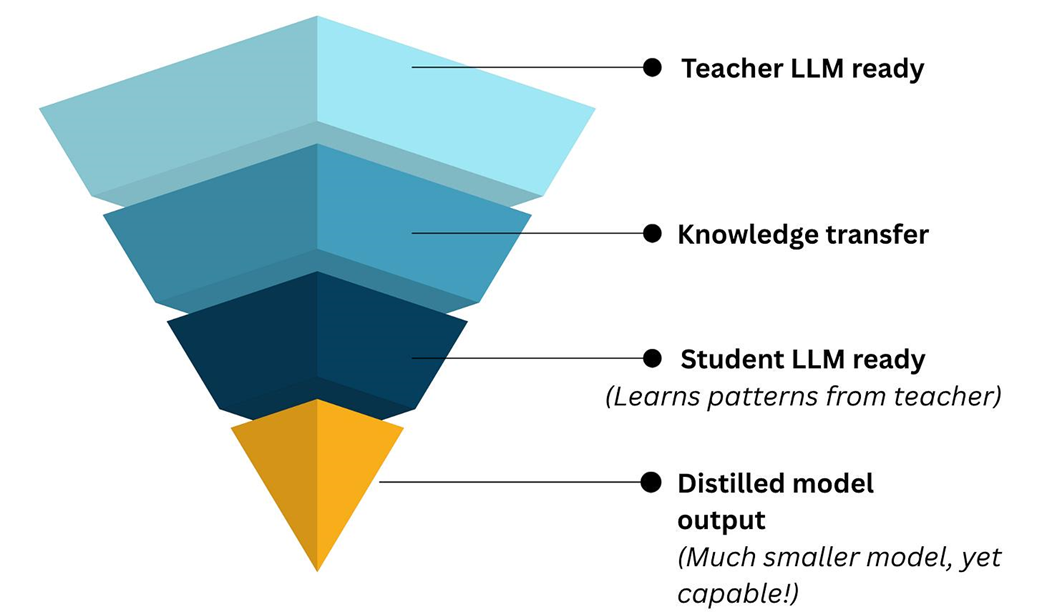
The concept of knowledge distillation. A large, powerful "teacher" model (like DeepSeek-R1) is used to generate training data to teach a much smaller, more efficient "student" model, transferring its capabilities without the high computational cost.
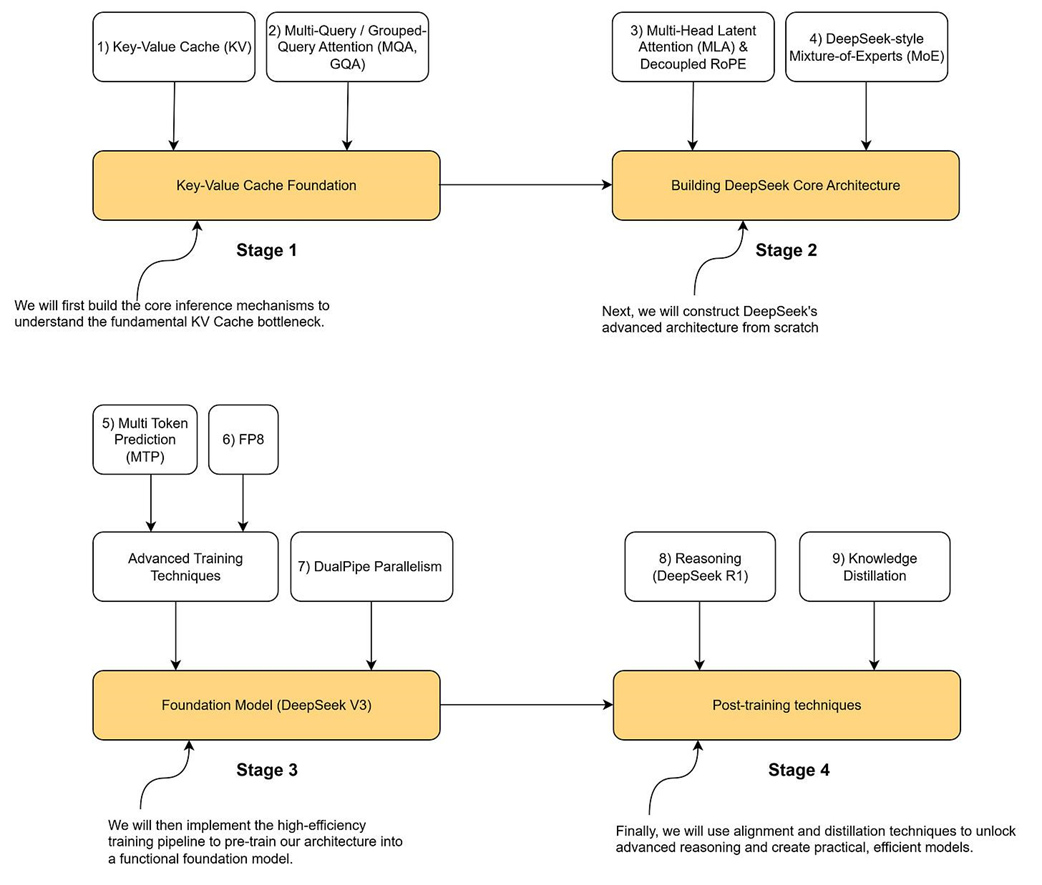
The four-stage roadmap for building a mini-DeepSeek model in this book. We will progress from foundational concepts (Stage 1) and core architecture (Stage 2) to advanced training (Stage 3) and post-training techniques (Stage 4), implementing each key innovation along the way.
Summary
- Large Language Models (LLMs) have become a dominant force in technology, but the knowledge to build them has often been confined to a few large labs.
- DeepSeek marked a pivotal moment by releasing open-source models with performance that rivaled the best proprietary systems, demonstrating that cutting-edge AI could be developed and shared openly.
- This book will guide you through a hands-on process of building a mini-DeepSeek model, focusing on its key technical innovations to provide a deep, practical understanding of modern LLM architecture and training.
- The core innovations we will implement are divided into four stages: (1) KV Cache Foundation, (2) Core Architecture (MLA & MoE), (3) Advanced Training Techniques (MTP & FP8), and (4) Post-training (RL & Distillation).
- By building these components yourself, you will gain not just theoretical knowledge but also the practical skills to implement and adapt state-of-the-art AI techniques.
 Build a DeepSeek Model (From Scratch) ebook for free
Build a DeepSeek Model (From Scratch) ebook for free