1 Governing Generative AI
Generative AI is transforming work across sectors, but its speed, scale, and unpredictability create risks that outstrip traditional controls. The chapter shows how incidents such as hallucinated legal citations, prompt-injection attacks, insecure integrations, model extraction, and persistent privacy issues (memorization and hard-to-undo training) are no longer edge cases. Because generative models are probabilistic, easily manipulated, and hard to remediate after failure, mistakes can spread instantly and publicly. Coupled with intensifying regulatory and contractual pressures (from data protection to sector rules and the EU AI Act), these factors make disciplined AI governance an immediate necessity rather than a future aspiration.
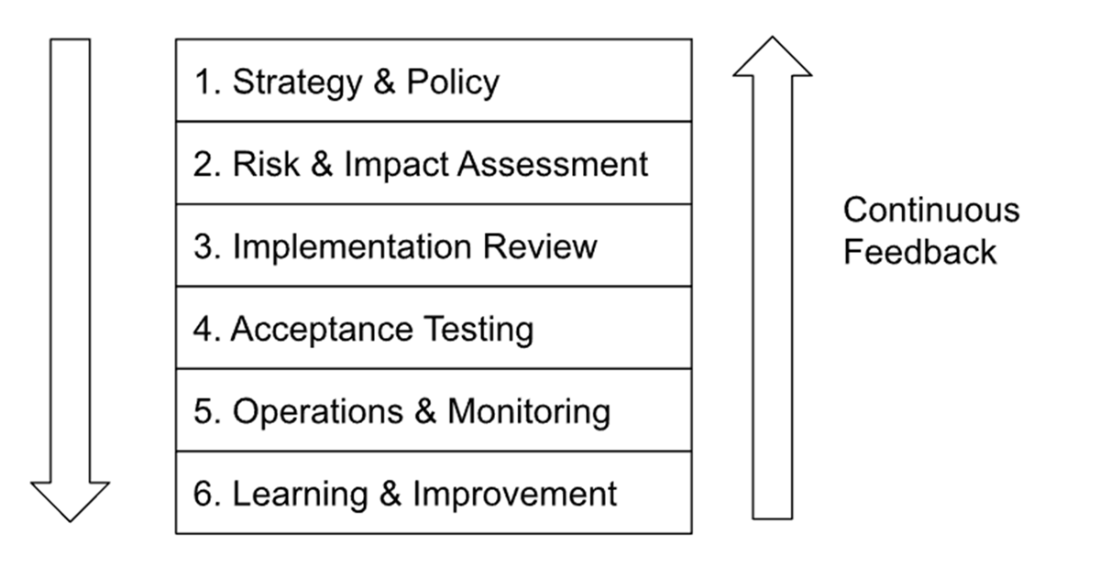
GRC for AI is presented as an enabler of innovation, not a box‑ticking brake. Governance sets direction and accountability; risk management continuously identifies, tests, and mitigates evolving technical and societal harms; compliance meets external rules and internal commitments, while recognizing that “formally compliant” is not the same as safe or trustworthy. The chapter argues for probabilistic, lifecycle-based oversight that adapts as systems learn and contexts shift, with responsibilities shared across the supply chain (model providers, integrators, and users). It introduces a practical six-level model that embeds controls end to end: Strategy & Policy; Risk & Impact Assessment; Implementation Review; Acceptance Testing; Operations & Monitoring; and Learning & Improvement—each a checkpoint to align value, document limits, harden designs, validate safety, monitor behavior, and feed lessons back.
Real and plausible cases—from call‑center copilots that misstate policy, to youth-facing chat assistants that bypass safeguards, to healthcare and security failures—illustrate how gaps at any level can trigger ethical, legal, and reputational damage. The chapter previews concrete practices that operationalize governance: threat modeling, red teaming, confidence scoring, grounding and selective human review, AI firewalls and output scanners, drift and anomaly detection, data and model lineage, bias and toxicity testing, retention controls, incident response, and continuous metrics (including trust signals). Anchored by emerging standards like ISO 42001 and risk frameworks, the message is clear: early, proportionate, and continuous GRC reduces likelihood and impact of failures, protects privacy and IP, sustains regulatory readiness, and—most importantly—makes innovation with generative AI reliable and defensible.
Generative models such as ChatGPT can often produce highly recognizable versions of famous artwork like the Mona Lisa. While this seems harmless, it illustrates the model's capacity to memorize and reconstruct images from its training data; a capability that becomes a serious privacy risk when the training data includes personal photographs.

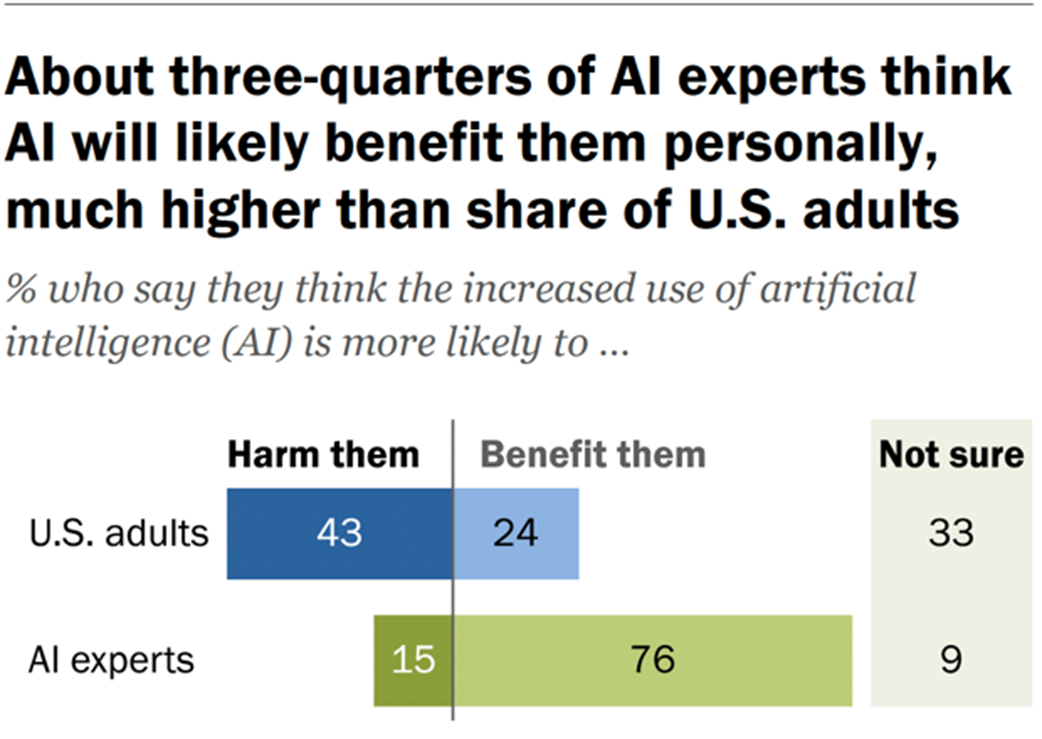
Trust in AI: experts vs general population. Source: Pew Research Center[46].
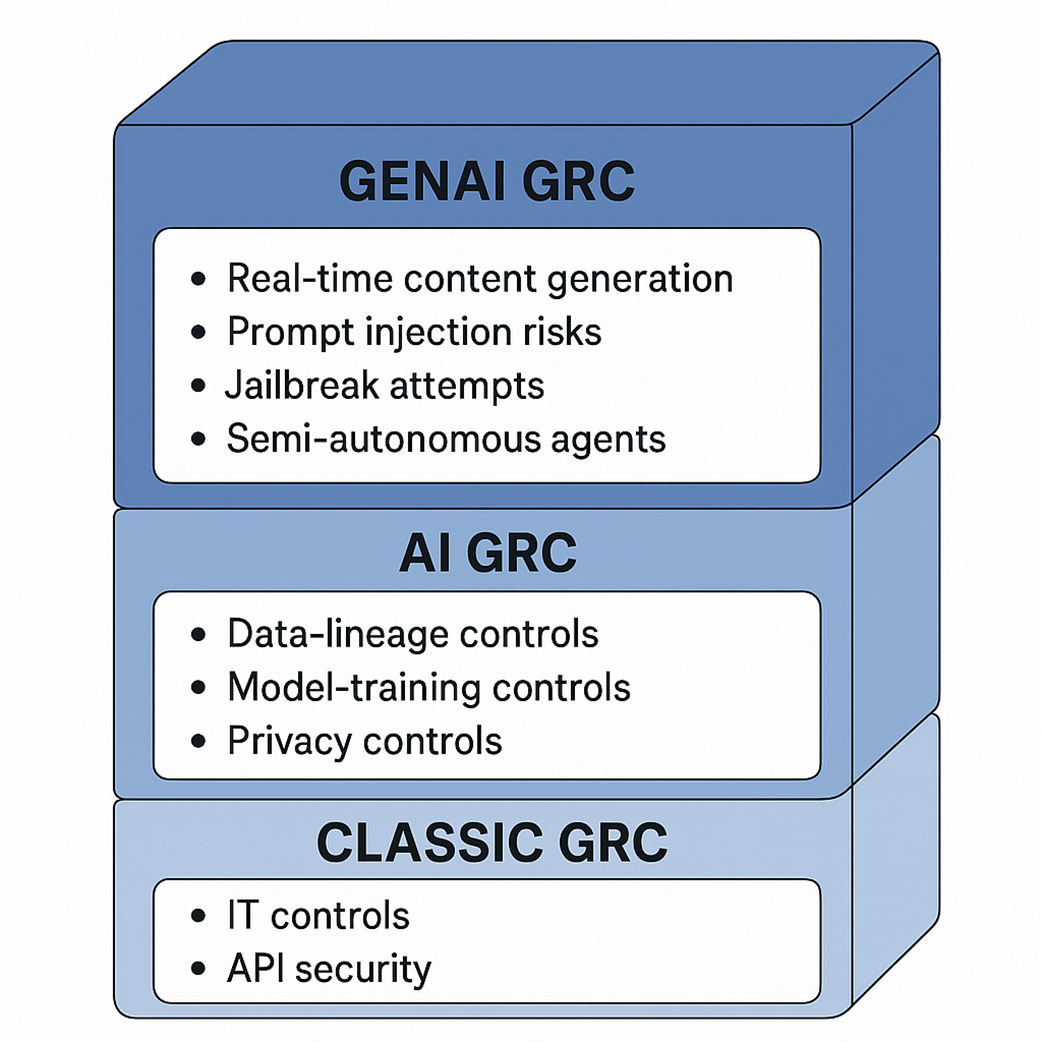
Classic GRC compared with AI GRC and GenAI GRC
Six Levels of Generative AI Governance. Chapter 2 will expand into what control tasks attach to each checkpoint.
Conclusion: Motivation and Map for What’s Ahead
By now, you should be convinced that governing AI is both critically important and uniquely challenging. We stand at a moment in time where AI technologies are advancing faster than the governance surrounding them. There’s an urgency to act: to put frameworks in place before more incidents occur and before regulators force our hand in ways we might not anticipate. But there’s also an opportunity: organizations that get GenAI GRC right will enjoy more sustainable innovation and public trust, turning responsible AI into a strength rather than a checkbox.
In this opening chapter, we reframed GRC for generative AI not as a dry compliance exercise, but as an active, risk-informed, ongoing discipline. We introduced a structured governance model that spans the AI lifecycle and multiple layers of risk, making sure critical issues aren’t missed. We examined real (and realistic) examples of AI pitfalls: from hallucinations and prompt injections to model theft and data deletion dilemmas. We have also provided a teaser of the tools and practices that can address those challenges, giving you a sense that yes, this is manageable with the right approach.
As you proceed through this book, each chapter will dive deeper into specific aspects of AI GRC using case studies. We’ll tackle topics like establishing a GenAI Governance program (Chapter 2). We will then address different risk areas such as security & privacy (Chapter 3) and trustworthiness (Chapter 4). We’ll also devote time to regulatory landscapes, helping you stay ahead of laws like the EU AI Act, and to emerging standards (you’ll hear more about ISO 42001, NIST, and others). Along the way, we will keep the tone practical – this is about what you can do, starting now, in your organization or projects, to make AI safer and more reliable.
By the end of this book, you'll be equipped to:
- Clearly understand and anticipate GenAI-related risks.
- Implement structured, proactive governance frameworks.
- Confidently navigate emerging regulatory landscapes.
- Foster innovation within a secure and ethically sound AI governance framework.
Before we move on, take a moment to reflect on your own context. Perhaps you are a product manager eager to deploy AI and thinking about how the concepts here might change your planning. Or you might be an executive worried about AI risks and consider where your organization has gaps in this new form of governance. Maybe you are a compliance professional or lawyer and ponder how a company’s internal GRC efforts could meet or fall short of your expectations. Wherever you stand, the concepts in this book aim to bridge the gap between AI’s promise and its risks, giving you the knowledge to maximize the former and mitigate the latter. By embracing effective AI governance now, you not only mitigate risks. You position your organization to lead responsibly in the AI era.
FAQ
Why does GenAI governance matter right now?
Because GenAI failures can be fast, large-scale, and public. Incidents like hallucinated legal citations, injected “memories” in assistants, data exposures, and disinformation are rising while adoption accelerates. Governance reduces the likelihood and impact of these failures, protecting people, reputation, and compliance—and avoids costly “fix later” scenarios that may be impossible with models.How does GenAI differ from classical software or human processes, and why do old controls break?
GenAI is probabilistic, context-dependent, and susceptible to both software-style exploits (prompt injection, data poisoning) and human-like manipulation. Compared to classical software, remediation is harder, behavior is less predictable, and failures can look convincing. Detection is opaque (root causes buried in model weights), so traditional point-in-time tests and static controls aren’t enough.What is GRC in the context of GenAI?
- Governance: Leadership, policies, and accountability that align AI with strategy and acceptable risk.- Risk Management: Continuously identifying, assessing, and mitigating technical, ethical, and societal risks across the lifecycle.
- Compliance: Adhering to laws, regulations, and internal policies. Compliance is the floor, not the ceiling; being “formally compliant” doesn’t guarantee safety or trust.
What is the six-level GenAI Governance (6L-G) model?
- Strategy & Policy: Charters, principles, and executive ownership of AI risk.- Risk & Impact Assessment: Classify use-case risk, map mitigations, and make go/no-go decisions (including “don’t use AI”).
- Implementation Review: Threat modeling, privacy-by-design, secure architectures, and documentation before build.
- Acceptance Testing: Independent verification—red teaming, safety/bias testing, privacy checks—before launch.
- Operations & Monitoring: Runtime guardrails, drift/toxicity monitoring, incident response, and decommissioning.
- Learning & Improvement: Feedback loops, KPIs, audits, and policy/process updates.
What GenAI failure modes does the chapter highlight?
- Hallucinations: Confident but false output (e.g., fabricated crimes or legal citations).- Prompt attacks: Jailbreaks and injections that hijack behavior or actions (e.g., hidden instructions in content or memory).
- Data poisoning/adversarial inputs: Subtle changes that mislead models (e.g., medical imaging pixel tweaks).
- Model extraction: API query harvesting to clone models and steal IP.
- Privacy leakage/memorization: Models reproducing training data (text or images) verbatim.
- Bias/discrimination: Unequal outcomes in hiring, services, or content generation.
- Disinformation: Rapid creation and spread of synthetic media.
How should organizations handle privacy and data protection with GenAI?
- Expect memorization and leakage risks; anonymization is hard to guarantee.- “Right to be forgotten” is challenging—machine unlearning is immature; retraining may be required.
- Avoid repurposing personal data without a valid legal basis and clear notice/consent.
- Build for erasure end-to-end (data maps, pseudonymization, model versioning, retraining plans, audit logs).
- Treat vendor data retention, logs, and model checkpoints as in-scope for privacy.
What does the chapter say about regulations and accountability?
- EU AI Act: Regulates high-risk uses and certain general-purpose models; requires technical documentation and training-data summaries; adds checks for systemic-risk models.- U.S.: Patchwork enforcement (e.g., FTC, FDA, CFPB, state privacy and AI laws).
- Upstream vendors must govern models; downstream buyers inherit and contractually enforce obligations—market and regulators punish weak upstream governance.
When should teams say “don’t use AI,” and how are go/no-go decisions made?
During Risk & Impact Assessment, weigh value versus governance overhead and downside risk. If mitigations are unfunded or risks remain unacceptable (e.g., regulated domains like healthcare without controls), choose “no-go” or redesign. Any residual risk must be explicitly accepted and escalated to leadership.Which tools and practices help operationalize GenAI GRC?
- Strategy & Policy: Responsible AI charters, risk tiers, cross-functional committees.- Risk & Impact Assessment: Regulatory checklists, impact templates, third-party risk reviews.
- Implementation Review: Threat modeling, AI firewalls, data minimization, CMEK, model/system cards.
- Acceptance Testing: Red-teaming and eval tools (e.g., Promptfoo, Garak, PyRIT, ART), load tests, bias tests.
- Operations & Monitoring: Output scanners, drift dashboards, MLFlow, incident playbooks.
- Learning & Improvement: Trust-score dashboards, calibration/robustness metrics, lessons-learned.
 AI Governance ebook for free
AI Governance ebook for free