1 Artificial intelligence in IT
Generative AI is presented as a transformative force for IT, moving from hype to daily impact and rapidly becoming required knowledge. The text traces the leap in capability from early chatbots to modern multimodal, higher-reasoning systems, and surveys leading tools for text and images. Throughout, it emphasizes augmentation over replacement: AI excels at speed and breadth, but the best outcomes come from pairing models with human judgment, context, and creativity.
Concrete, work-ready applications span data extraction from documents, anomaly detection in logs, root cause analysis, analytics, disaster recovery planning, performance reviews, email drafting, and scripting across Bash, Python, and PowerShell. Beyond task automation, AI elevates roles—helping with project management practices, documentation, and communication—and can even act as a neutral facilitator to improve teamwork, as seen in rewriting contentious reports into objective, process-focused narratives. Access is broad via free tiers and low-cost API playgrounds, with paid options offering more capacity and enterprise features.
Responsible adoption is a recurring theme: safeguard sensitive data, prefer enterprise or private deployments when needed, and apply bias and fairness checks in workflows like hiring. The chapter cautions against overreliance on AI writing detectors, encourages transparent attribution and citation practices, and promotes using AI as an editorial collaborator rather than a ghostwriter. Finally, it sets the expectation that skillful use—progressing from simple prompts to precise problem formulation—will define professional advantage, enabling IT teams to automate routine work, improve decisions, and collaborate more effectively.
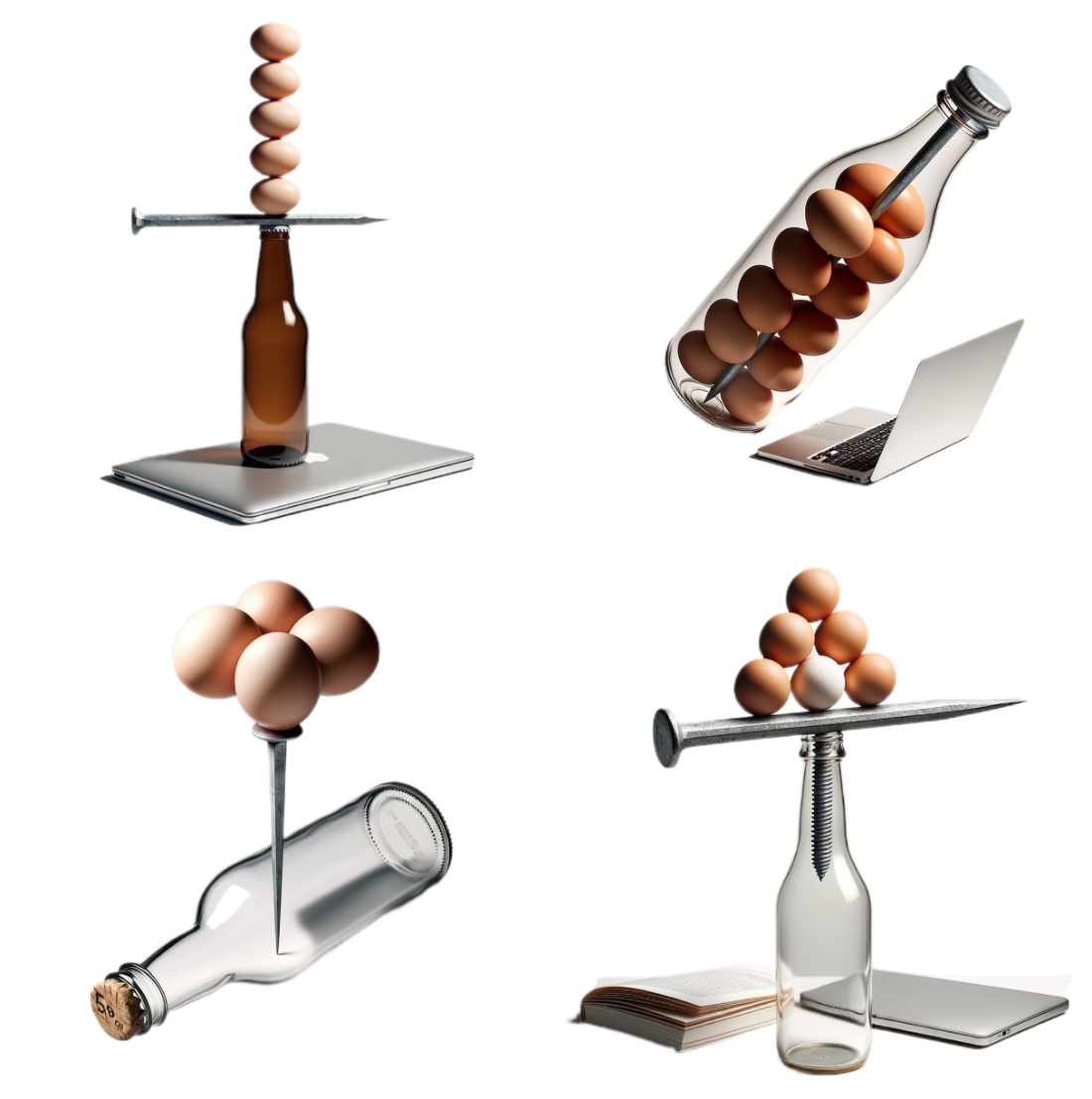
Intentionally impossible stacking by OpenAI’s DALL·E 3 image generator

Spiral Town

Citation prompt in ChatGPT
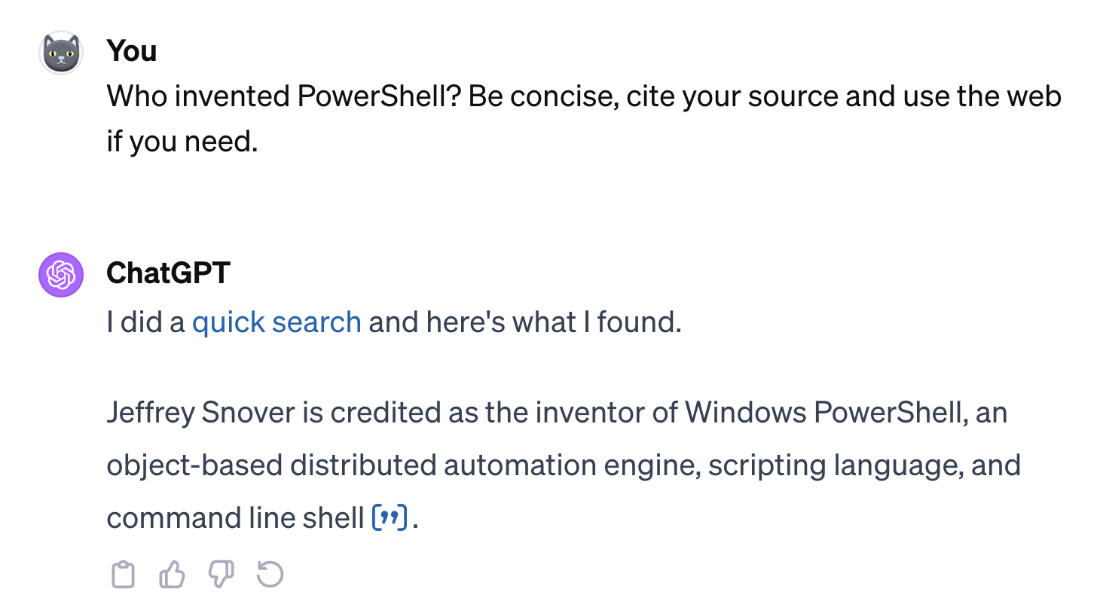
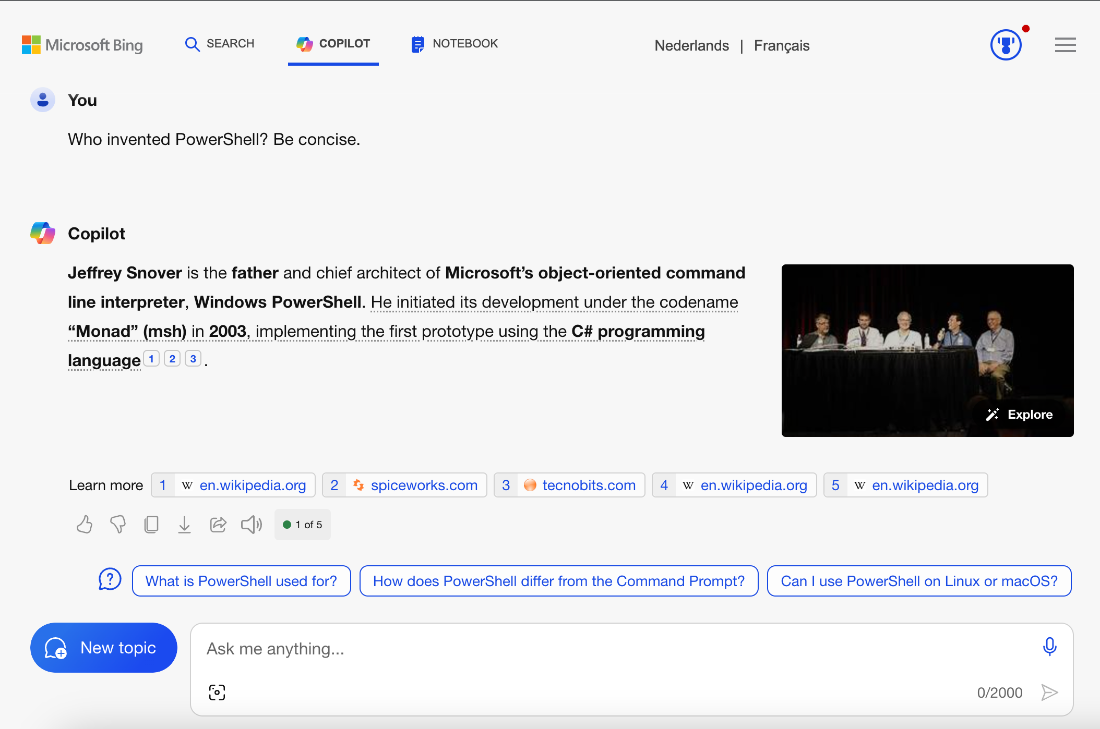
Default citation in Microsoft Copilot
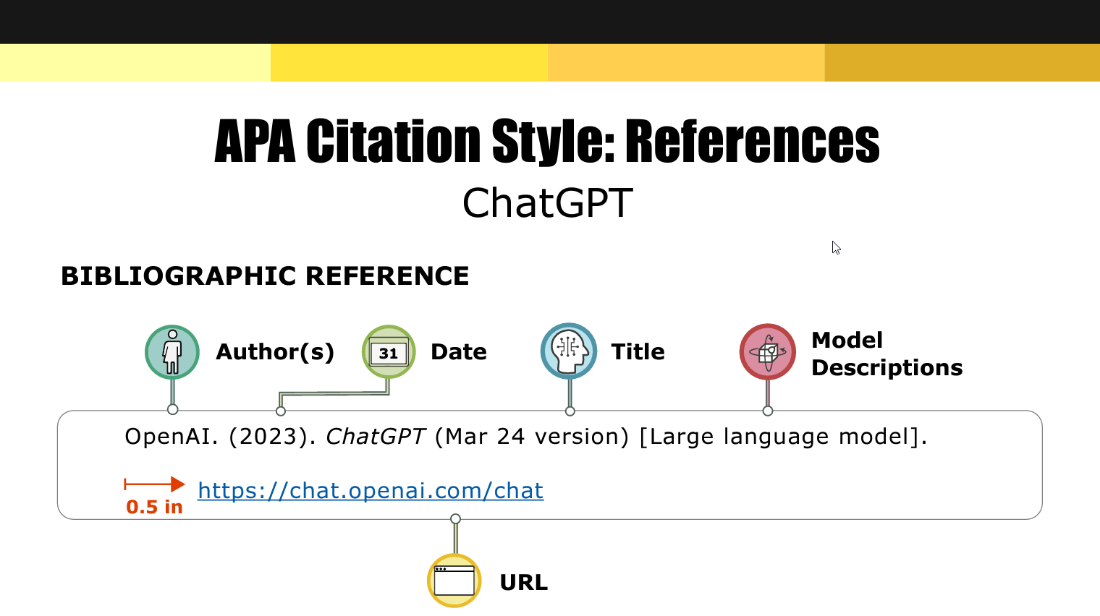
APA citation [1]
Prompts used in this chapter
Below are concrete examples of how we used AI to write this chapter. We’ll be including prompts like these at the end of all chapters in this book, in hopes that they’ll help you get ideas for how to use AI in your own work.
- Name 50 real-world, practice things you think this book could help IT Professionals. For example "Generate After-Action Reports with objective insights, removing all intrapersonal issue influence"
- Give me 10 suggestions that can replace the phrase "in a setting"
- Can you suggest a change to the second paragraph that emphasizes fun and also give me a stronger call to action at the end
- "Amidst a backdrop of technical hurdles" sounds haughty. Can you use smaller words?
- I’m about to paste two paragraphs and I want to keep them as is but insert a story in the middle. I’ll paste a story told in first person but please change it to third person.
- Fix the transition from the paragraph to the list
- Here is a revised Chapter 1. Please review it and give me some insights. Anything I missed that can make it a little longer?
FAQ
What is generative AI and how does it apply to everyday IT work?
Generative AI creates new content (text, images) by learning patterns from data. In IT, text models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini can draft policies, documentation, scripts, RCAs, DR plans, and analytics summaries. Image models like DALL-E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion quickly produce illustrations and presentation graphics.
Will AI replace IT professionals?
No. AI augments skilled professionals rather than replaces them. The advantage goes to IT pros who learn to use AI effectively. Knowing how to ask the right questions, validate outputs, and implement solutions remains essential.
Which AI chatbots and models should IT pros know, and how do they differ?
- ChatGPT (OpenAI): Strong generalist; improved reasoning, voice, and vision in newer versions.
- Claude (Anthropic): Safety-focused, nuanced analysis, handles long documents well.
- Gemini (Google): Tight integration with Google Workspace (Gmail, Docs, Drive, etc.).
- Microsoft Copilot: Deep Microsoft 365 integration (Outlook, Teams, SharePoint).
- Image engines: DALL-E (versatile), MidJourney (photorealistic portraits), Stable Diffusion (open-source, customizable).
What high-impact IT use cases are ready right now?
- Data extraction: Move data from PDFs to databases in minutes.
- Root cause analysis: Upload logs and iteratively question to isolate causes.
- Analytics: Summarize large datasets into manager-ready insights.
- Disaster recovery planning: Generate draft DR plans from system inventories.
- Performance reviews: Structure fair reviews and SMART goals.
- Scripting: Generate Bash, PowerShell, and Python for routine admin tasks.
How does AI help with security and incident response?
AI can flag anomalies in logs and user behavior in near real time, helping teams detect issues earlier. It accelerates triage and frees humans to focus on higher-value work (for example, improving backup testing). Pair AI’s speed with human judgment; AI cannot replace human context or empathy.
Can AI improve collaboration, communication, and cross-team workflows?
Yes. AI can rewrite contentious reports (like AARs) into neutral, systems-focused narratives, suggest blameless postmortem language, draft professional emails, route tickets by skills, and guide lightweight project management (problem statements, methodology choices, and documentation).
What guidelines should I follow to use AI responsibly with company data?
- Follow your organization’s AI policy; do not paste confidential data into public tools.
- Use enterprise or private options (for example, OpenAI Enterprise, Microsoft 365 Chat, Azure OpenAI) with proper security controls.
- Encrypt, minimize data sharing, and prefer on-tenant integrations when available.
- Audit outputs and keep a human in the loop for critical decisions.
How do I reduce bias and ensure fairness when using AI (for example, in hiring)?
- Standardize interviews and anonymize resumes.
- Use diverse review panels and skills-based assessments.
- Check outputs with tools (for example, Textio) and review for biased language.
- Track decisions for patterns and continuously refine prompts and processes.
What should I know about costs, free tiers, and API playgrounds?
- Most major tools offer free tiers with usage limits (for example, Claude ~10 messages per 5 hours).
- Typical subscriptions: ChatGPT Plus $20/month; Gemini $19.99/month (often bundled with storage); Claude Pro $20/month; Copilot Pro $20/month; Copilot for Microsoft 365 $30/month; GitHub Copilot $10/month; MidJourney from $10/month; DALL-E included with ChatGPT Plus.
- API playgrounds can be cheaper for light usage (many users spend about $2–$6/month in tokens).
Can AI-written content be reliably detected, and how should I cite AI use?
- Reliable detection is not currently possible; even OpenAI discontinued its detector.
- Prefer tools that can cite sources on request (for example, ChatGPT, Copilot, Gemini). Claude does not browse/cite by default; treat its outputs as generated guesses.
- Be transparent: acknowledge how AI assisted your work. Many institutions advise referencing the tool (for example, cite ChatGPT/OpenAI) and noting prompts in-text since outputs are non-recoverable.
 AI for Everyday IT ebook for free
AI for Everyday IT ebook for free