1 Large Language Models and the Need for Retrieval Augmented Generation
Large Language Models have rapidly become central to modern AI applications, yet their impressive fluency masks practical limits that affect reliability. This chapter introduces Retrieval Augmented Generation as a pragmatic way to strengthen LLMs by supplying relevant, external information at query time. It sets expectations for the book: define RAG, explain why it’s needed, outline how LLMs work and are used, and preview how RAG-enabled systems are designed, so readers gain the foundation to explore RAG’s components in depth.
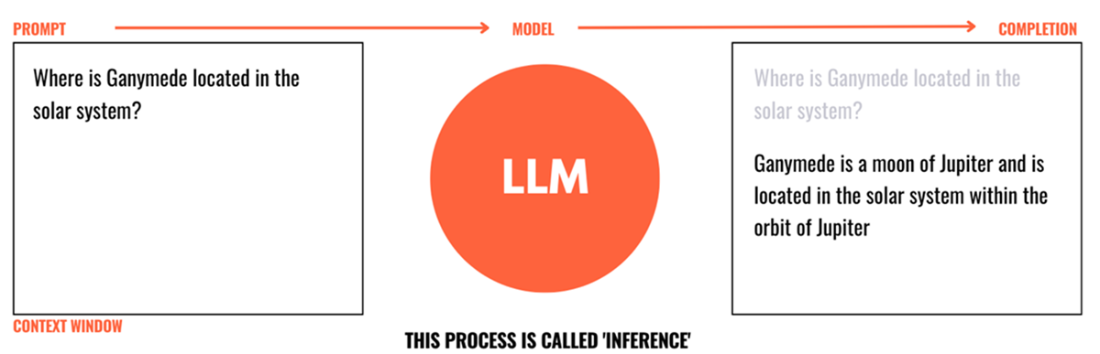
LLMs are next‑token predictors trained on vast text corpora, typically with transformer architectures, and are often consumed as foundation models. Users interact through prompts to obtain completions during inference, with prompt engineering (roles, examples/few‑shot, structured reasoning strategies) improving results. Key operational concepts include context windows, temperature, in‑context learning versus supervised fine‑tuning, and the trade‑offs of small versus large models. These systems already power diverse tasks such as writing, summarization, translation, code generation, information extraction, classification, and conversational interfaces.
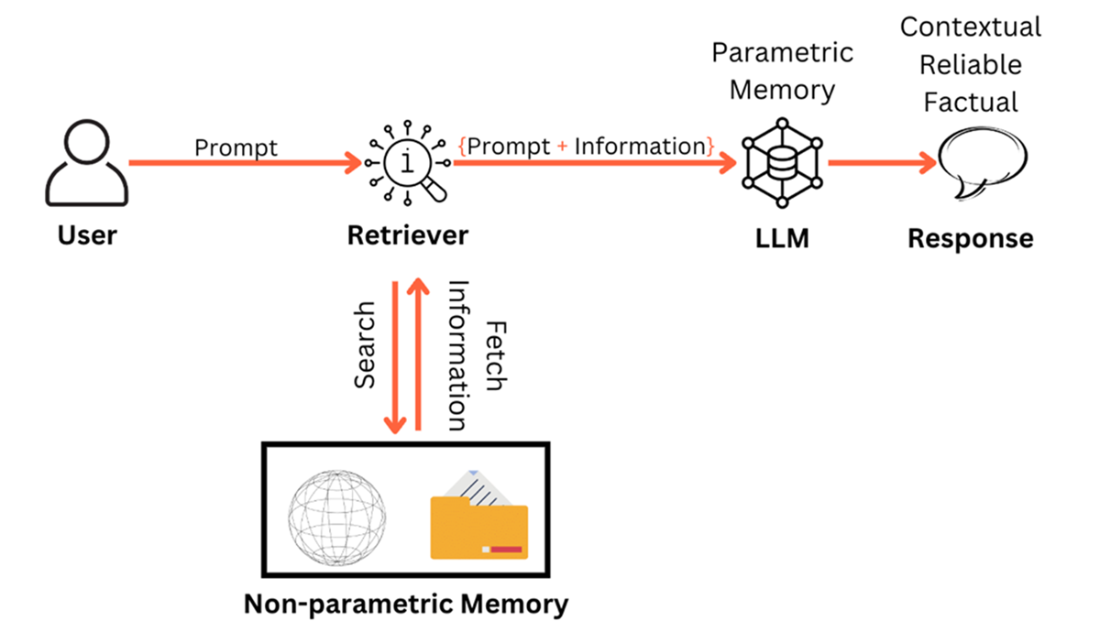
Despite their breadth, LLMs suffer from knowledge cutoffs, hallucinations, and lack of access to proprietary or up‑to‑date information. RAG addresses these gaps by retrieving pertinent content from external sources, augmenting the prompt, and then generating grounded answers—effectively extending an LLM’s parametric memory with a flexible non‑parametric memory. This reduces hallucinations, enables source citation, and makes responses more contextual and trustworthy, often at far lower cost than continual pretraining or fine‑tuning. The chapter highlights prominent RAG applications, including modern search experiences, personalized content, real‑time event commentary, support chatbots, document question answering, virtual assistants, and AI‑assisted research, underscoring RAG’s role in making LLMs practical and dependable.
ChatGPT response to the question, “Who won the 2023 cricket world cup?” (Variation 1), Source: Screenshot by author of his account on https://chat.openai.com
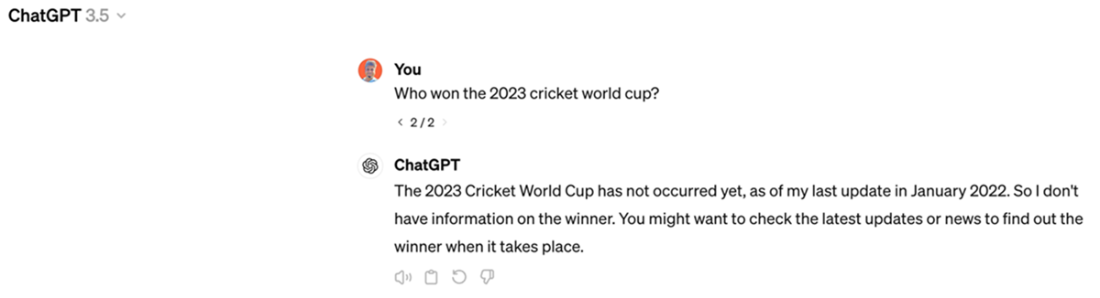
ChatGPT response to the question, “Who won the 2023 cricket world cup?” (Variation 2), Source: Screenshot by author of his account on https://chat.openai.com
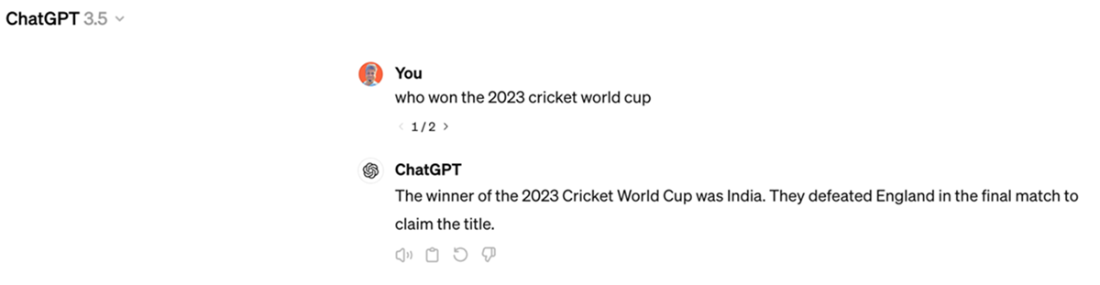
Wikipedia Article on 2023 Cricket World Cup, Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2023_Cricket_World_Cup
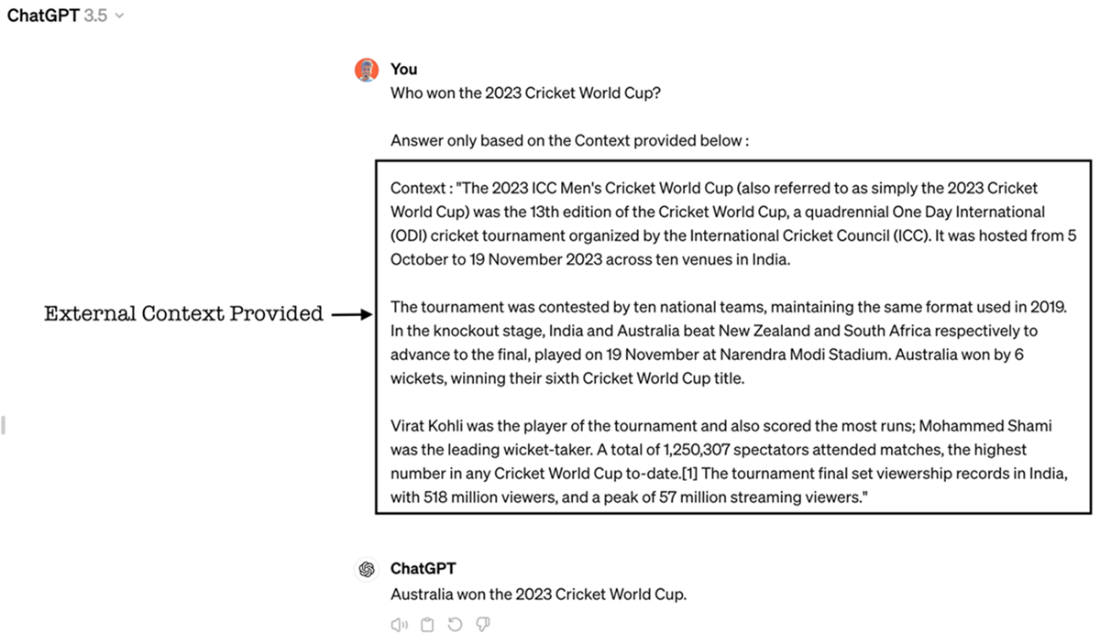
ChatGPT response to the question, augmented with external context, Source : Screenshot by author of his account on https://chat.openai.com
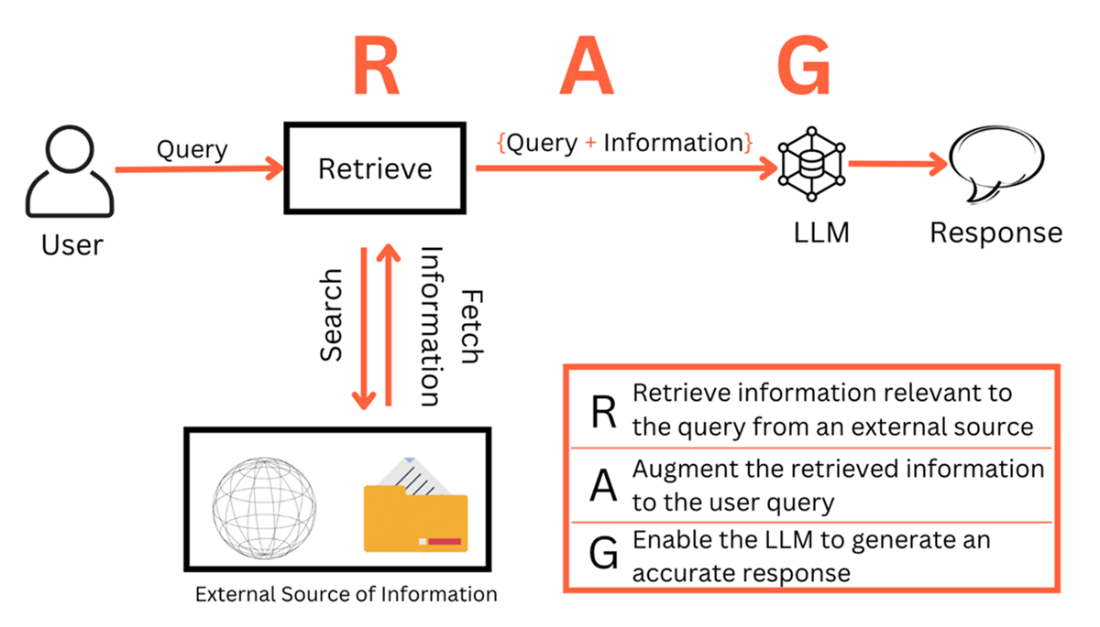
Retrieval Augmented Generation: A Simple Definition
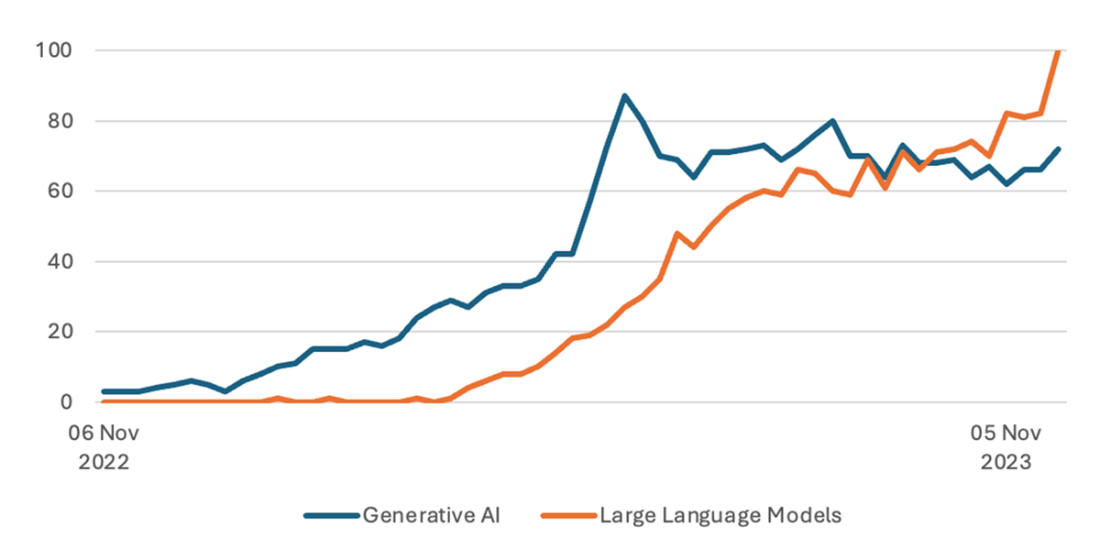
Google Trends of “Generative AI” and “Large Language Models” from Nov ’22 to Nov ‘23
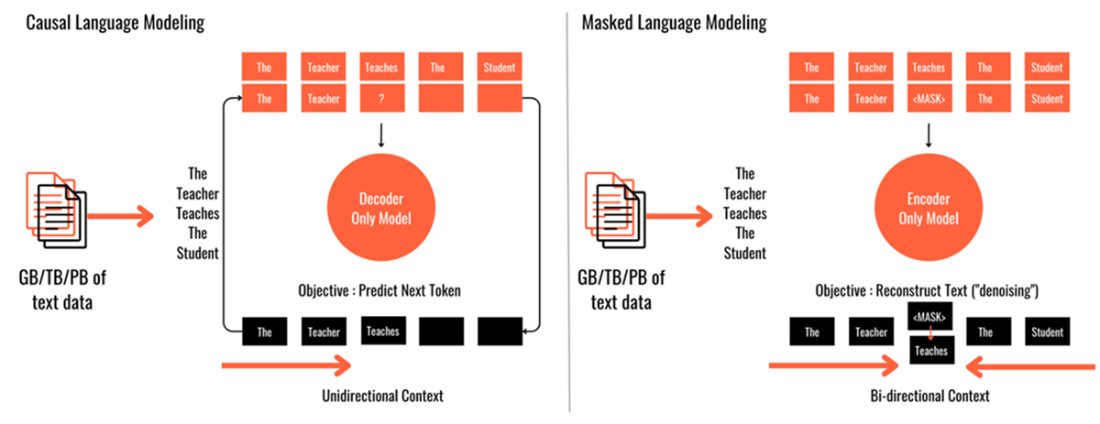
Two token prediction techniques – Causal Language Model & Masked Language Model
Illustrative probability distribution of words after “The Teacher”

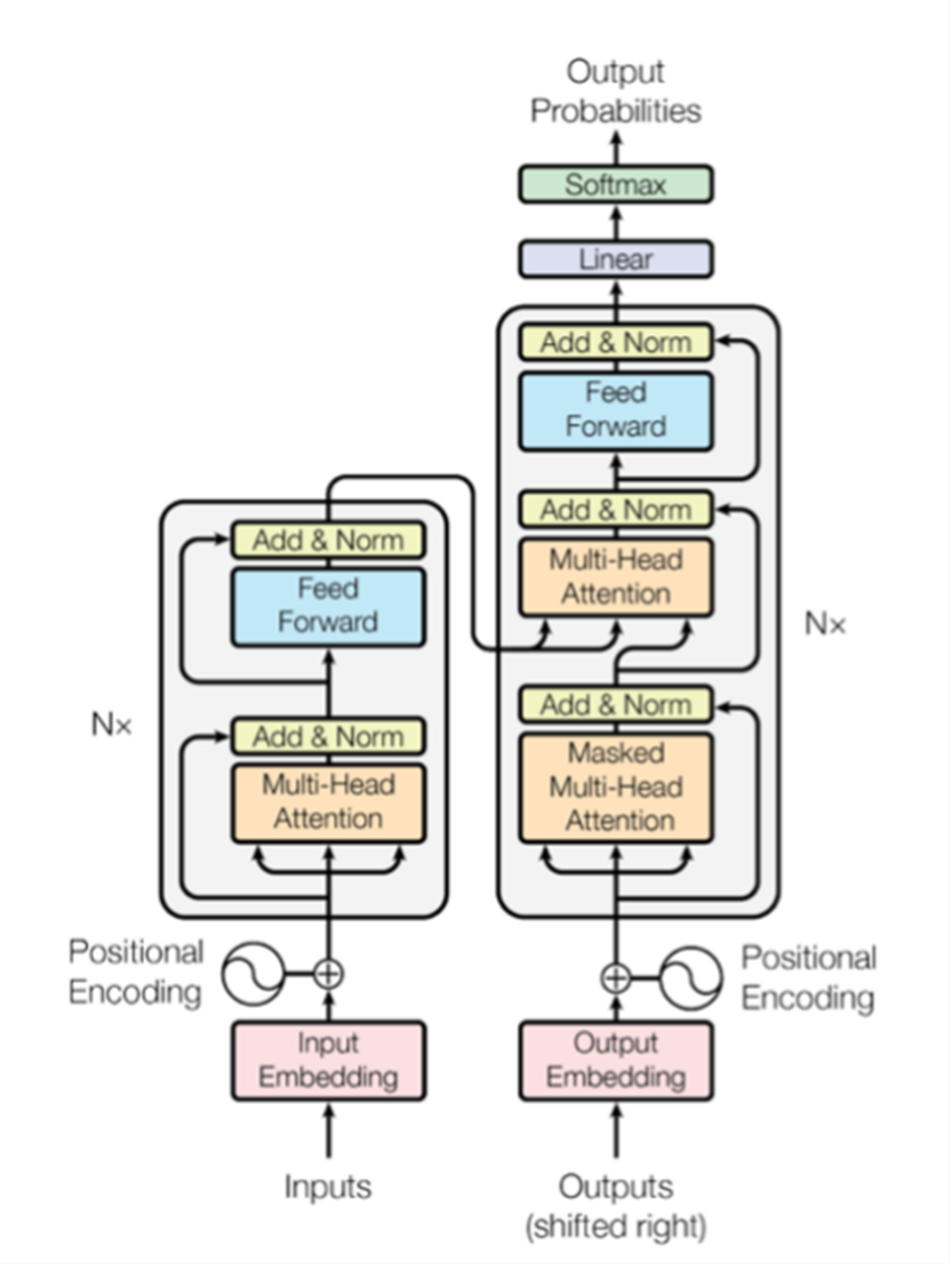
Transformer Architecture, Source: Attention is all you need, Vasvani et al.
Popular proprietary and open source LLMs as of April 2024 (non-exhaustive list)
Prompt, Completion, and Inference
RAG enhances the parametric memory of an LLM by creating access to non-parametric memory
Summary
- RAG enhances the memory of LLMs by creating access to external information.
- LLMs are next word, (or token) prediction models that have been trained on massive amounts of text data to generate human-like text.
- Interaction with LLMs is carried out using natural language prompts and prompt engineering is an important discipline.
- LLMs face challenges of having a knowledge cut-off date and being trained only on public data. They are also prone to generating factually incorrect information (hallucinations).
- RAG overcomes the limitations of the LLMs by incorporating non-parametric memory and increases the context awareness and reliability in the responses.
- Popular use cases of RAG are search engines, document question answering systems, conversational agents, personalized content generation, virtual assistants among others.
 A Simple Guide to Retrieval Augmented Generation ebook for free
A Simple Guide to Retrieval Augmented Generation ebook for free