1 Getting started with MLOps and ML engineering
Production machine learning succeeds or fails on engineering, not just modeling. This chapter sets the stage for building reliable, scalable ML systems by framing MLOps as the bridge from promising experiments to durable, value-delivering services. It positions the reader—whether a data scientist, software engineer, or ML engineer—to gain confidence through a hands-on, real-world approach that favors practical patterns over theory, covers the full lifecycle from ideation to operation, and emphasizes the mindset required to keep models healthy in the wild.
The chapter walks through the end-to-end ML lifecycle: deciding whether ML is warranted, framing the problem, collecting and labeling data, versioning datasets, training, evaluating, and validating with stakeholders. It highlights pipeline orchestration and automation for reproducibility and velocity, then explains the shift to dev/staging/production where CI/CD triggers end-to-end runs, models are deployed as versioned services (often containerized), and systems are tested for performance, scalability, and rollback. Ongoing monitoring spans system health, business outcomes, and data/model drift, with retraining scheduled or threshold-driven. The skills mix spans strong software engineering, practical ML familiarity, data engineering, and automation—anchored by an appreciation for ethics, security, and reliability.
With that foundation, the chapter introduces building an ML platform incrementally, centering on Kubeflow and Kubeflow Pipelines for orchestration, and expanding with components such as a feature store, a model registry, and automated deployment via CI/CD. It advocates learning by assembling the platform—even if you later adopt managed offerings—so you understand trade-offs and can tailor solutions. Tool choices are pragmatic and use-case driven, and the platform naturally extends to LLMOps with additions like vector search and guardrails. Three projects anchor the journey: an OCR system, a tabular movie recommender, and a RAG-powered documentation assistant, each reinforcing iterative workflows, changing requirements, and the reusable patterns needed to design, ship, monitor, and evolve production ML services.
The experimentation phase of the ML life cycle
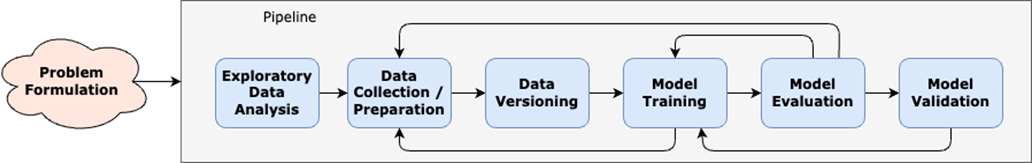
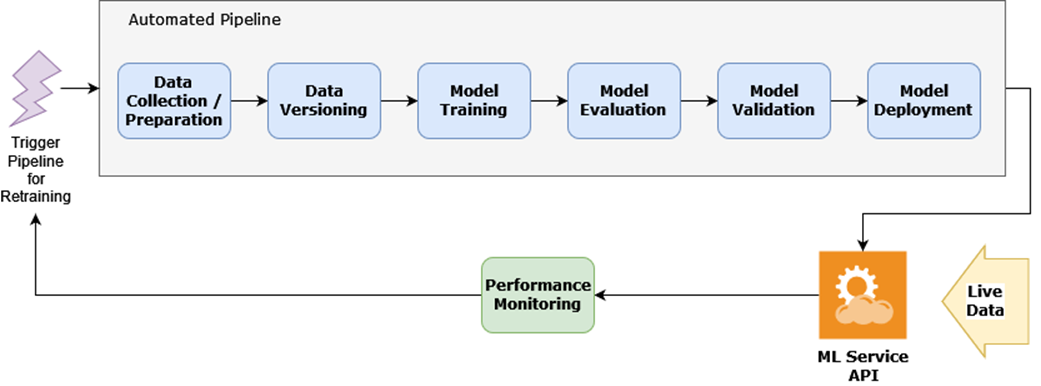
The dev/staging/production phase of the ML life cycle
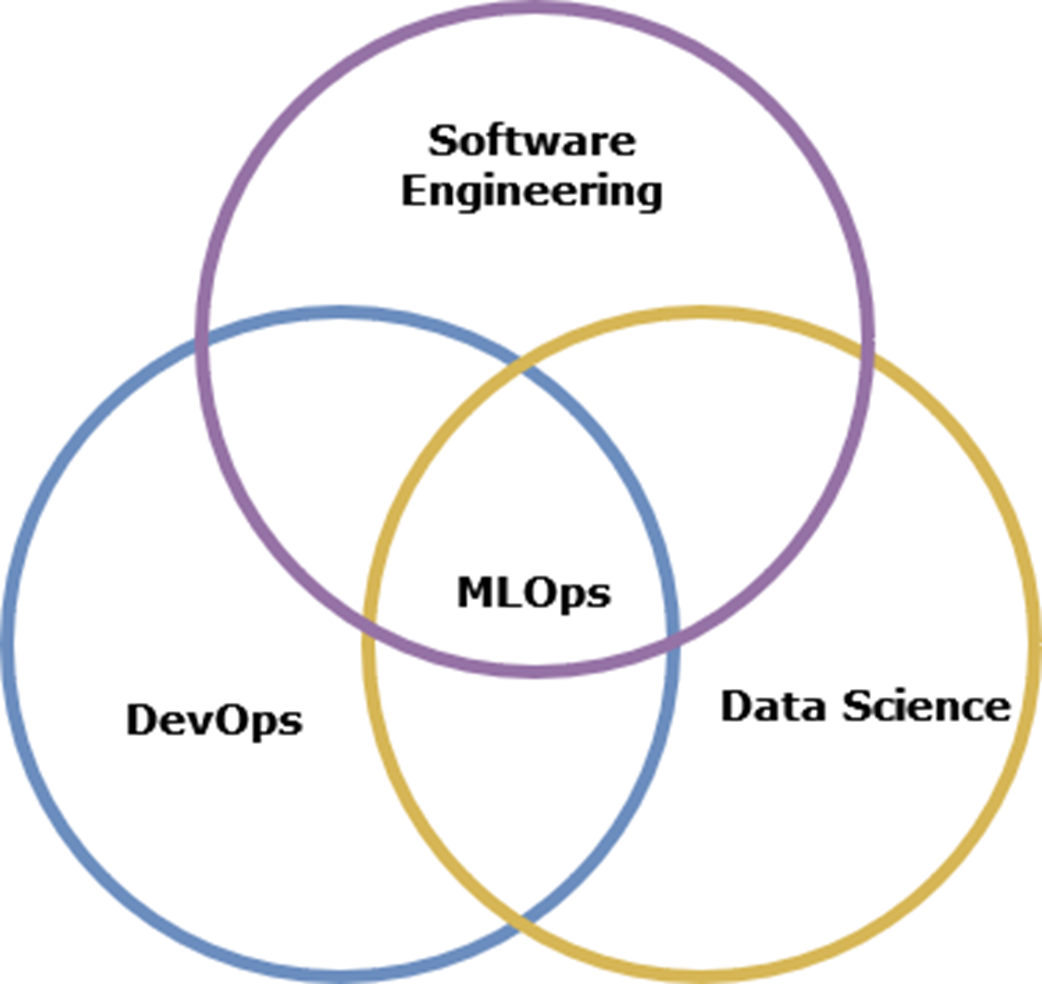
MLOps is a mix of different skill sets
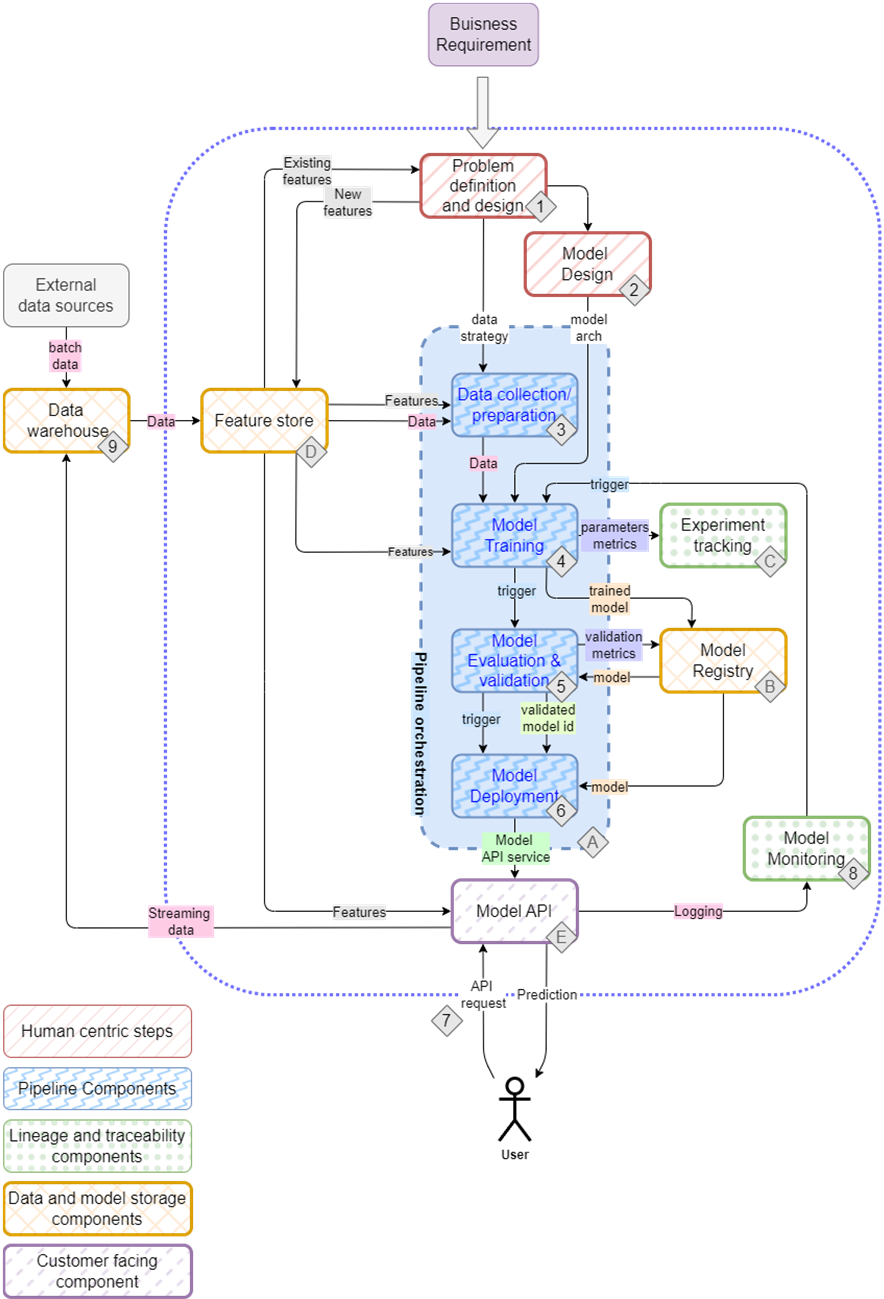
The mental map of an ML setup, detailing the project flow from planning to deployment and the tools typically involved in the process
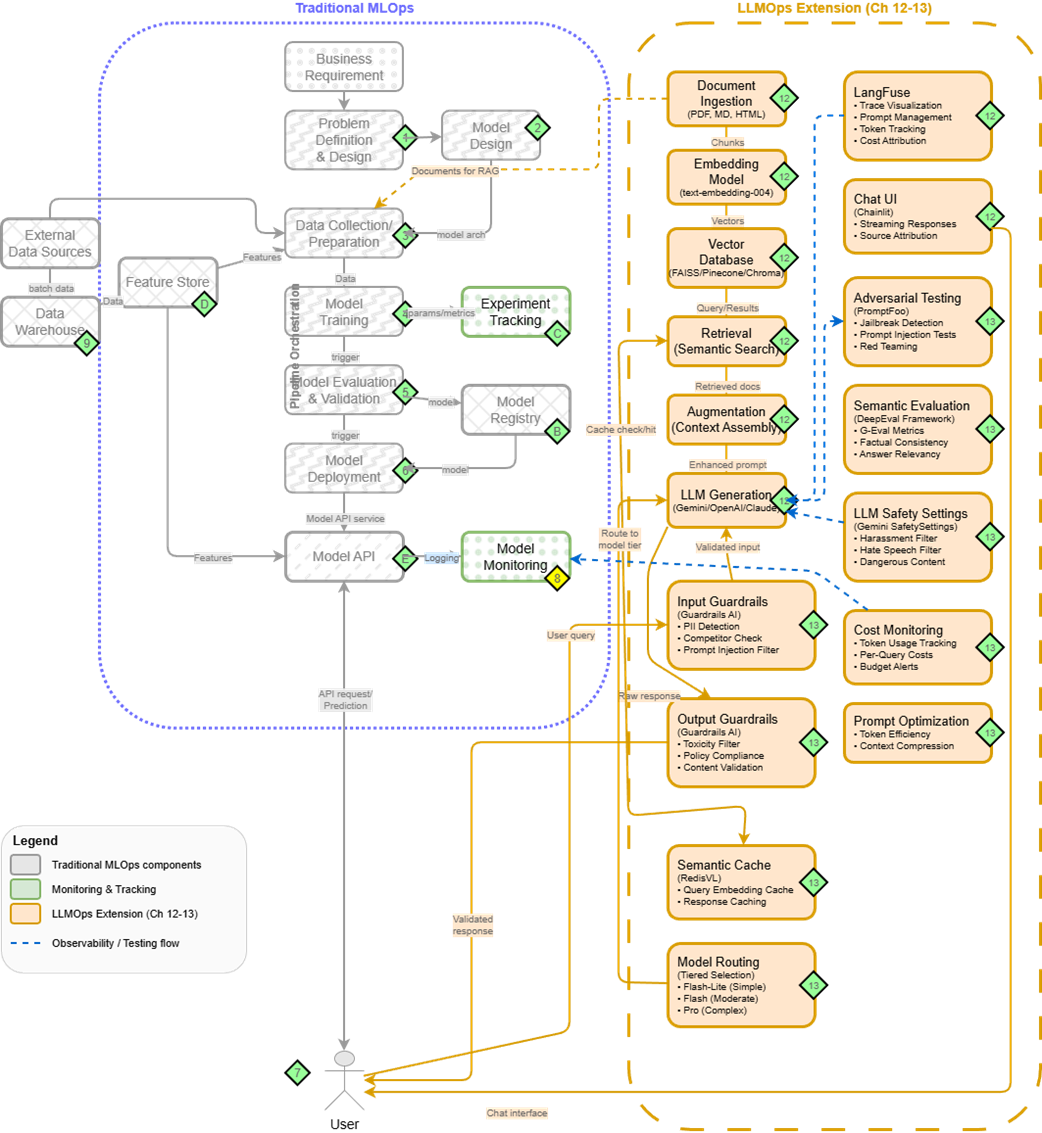
Traditional MLOps (right) extended with LLMOps components (left) for production LLM systems. Chapters 12-13 explore these extensions in detail.
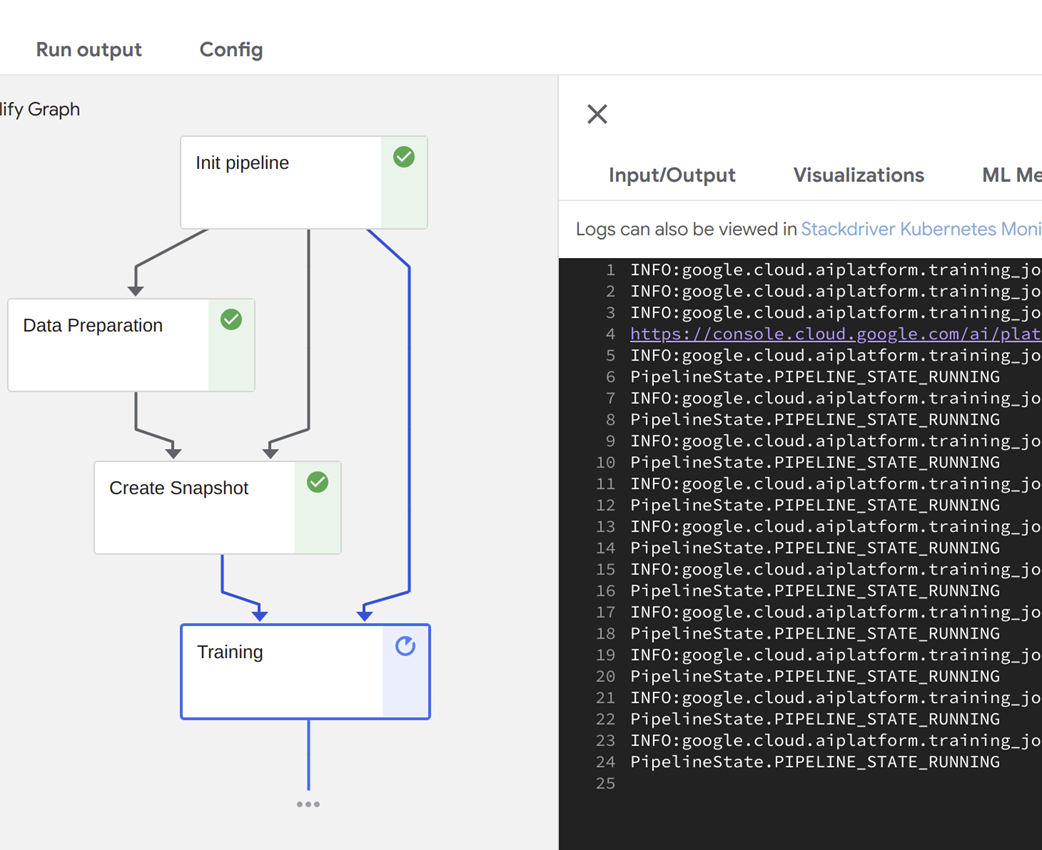
An automated pipeline being executed in Kubeflow.
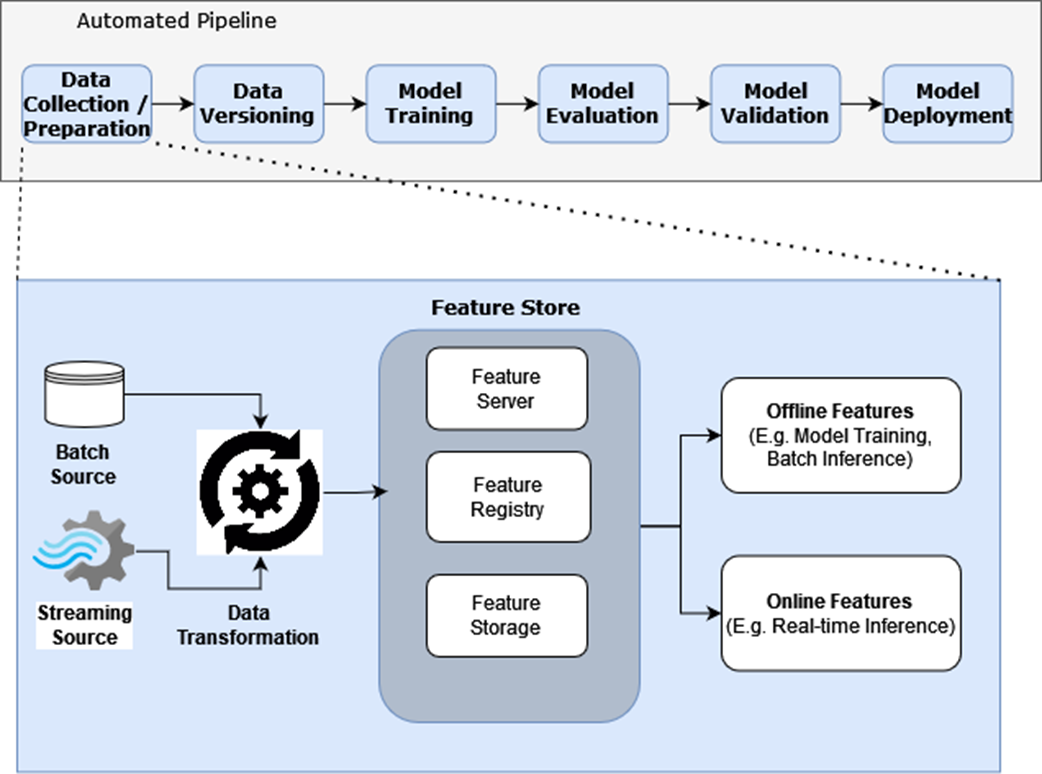
Feature Stores take in transformed data (features) as input, and have facilities to store, catalog, and serve features.
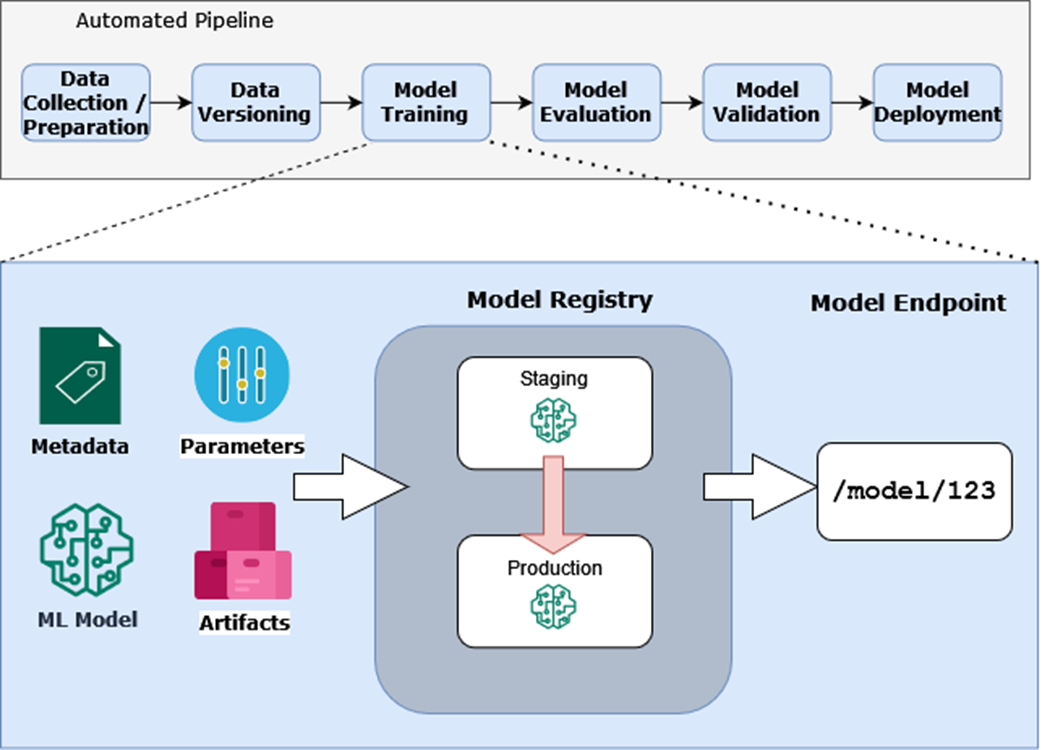
The model registry captures metadata, parameters, artifacts, and the ML model and in turn exposes a model endpoint.
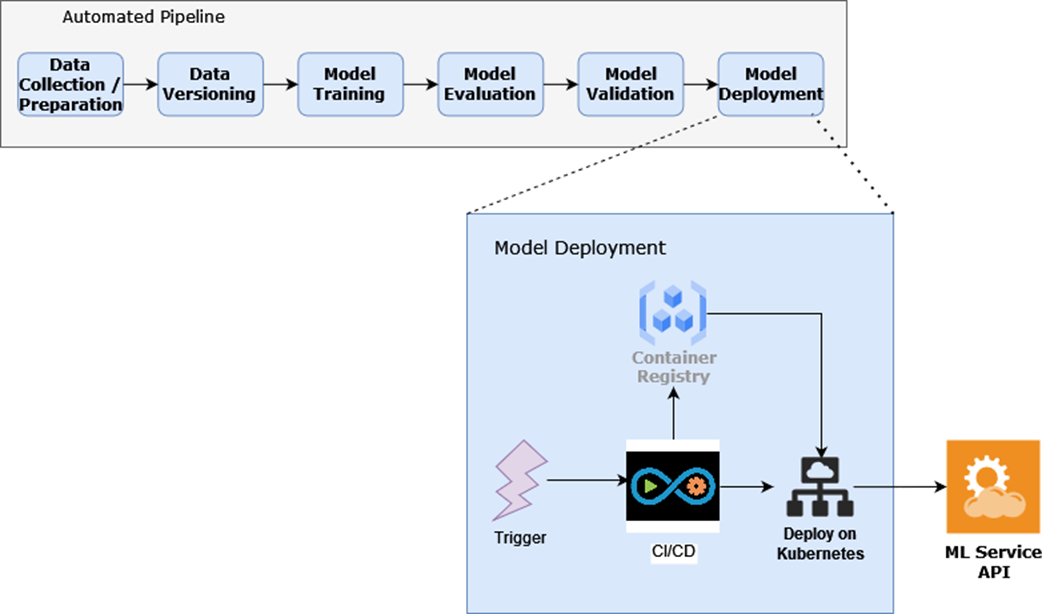
Model deployment consists of the container registry, CI/CD, and automation working in concert to deploy ML services.
Summary
- The Machine Learning (ML) life cycle provides a framework for confidently taking ML projects from idea to production. While iterative in nature, understanding each phase helps you navigate the complexities of ML development.
- Building reliable ML systems requires a combination of skills spanning software engineering, MLOps, and data science. Rather than trying to master everything at once, focus on understanding how these skills work together to create robust ML systems.
- A well-designed ML Platform forms the foundation for confidently developing and deploying ML services. We'll use tools like Kubeflow Pipelines for automation, MLFlow for model management, and Feast for feature management - learning how to integrate them effectively for production use.
- We'll apply these concepts by building two different types of ML systems: an OCR system and a Movie recommender. Through these projects, you'll gain hands-on experience with both image and tabular data, building confidence in handling diverse ML challenges.
- Traditional MLOps principles extend naturally to Large Language Models through LLMOps - adding components for document processing, retrieval systems, and specialized monitoring. Understanding this evolution prepares you for the modern ML landscape.
- The first step is to identify the problem the ML model is going to solve, followed by collecting and preparing the data to train and evaluate the model. Data versioning enables reproducibility, and model training is automated using a pipeline.
- The ML life cycle serves as our guide throughout the book, helping us understand not just how to build models, but how to create reliable, production-ready ML systems that deliver real business value.
 Build a Machine Learning Platform (From Scratch) ebook for free
Build a Machine Learning Platform (From Scratch) ebook for free